kornia.feature¶
Detectors¶
- kornia.feature.gftt_response(input, grads_mode='sobel', sigmas=None)¶
Compute the Shi-Tomasi cornerness function.

Function does not do any normalization or nms. The response map is computed according the following formulation:
\[R = min(eig(M))\]where:
\[\begin{split}M = \sum_{(x,y) \in W} \begin{bmatrix} I^{2}_x & I_x I_y \\ I_x I_y & I^{2}_y \\ \end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]- Parameters:
input (
Tensor) – input image with shape \((B, C, H, W)\).grads_mode (
str, optional) – can be'sobel'for standalone use or'diff'for use on Gaussian pyramid. Default:"sobel"sigmas (
Optional[Tensor], optional) – coefficients to be multiplied by multichannel response. Should be shape of \((B)\) It is necessary for performing non-maxima-suppression across different scale pyramid levels. See vlfeat. Default:None
- Return type:
- Returns:
the response map per channel with shape \((B, C, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.tensor([[[ ... [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], ... ]]]) # 1x1x7x7 >>> # compute the response map gftt_response(input) tensor([[[[0.0155, 0.0334, 0.0194, 0.0000, 0.0194, 0.0334, 0.0155], [0.0334, 0.0575, 0.0339, 0.0000, 0.0339, 0.0575, 0.0334], [0.0194, 0.0339, 0.0497, 0.0000, 0.0497, 0.0339, 0.0194], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0194, 0.0339, 0.0497, 0.0000, 0.0497, 0.0339, 0.0194], [0.0334, 0.0575, 0.0339, 0.0000, 0.0339, 0.0575, 0.0334], [0.0155, 0.0334, 0.0194, 0.0000, 0.0194, 0.0334, 0.0155]]]])
- kornia.feature.harris_response(input, k=0.04, grads_mode='sobel', sigmas=None)¶
Compute the Harris cornerness function.

Function does not do any normalization or nms. The response map is computed according the following formulation:
\[R = max(0, det(M) - k \cdot trace(M)^2)\]where:
\[\begin{split}M = \sum_{(x,y) \in W} \begin{bmatrix} I^{2}_x & I_x I_y \\ I_x I_y & I^{2}_y \\ \end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]and \(k\) is an empirically determined constant \(k ∈ [ 0.04 , 0.06 ]\)
- Parameters:
input (
Tensor) – input image with shape \((B, C, H, W)\).k (
Union[Tensor,float], optional) – the Harris detector free parameter. Default:0.04grads_mode (
str, optional) – can be'sobel'for standalone use or'diff'for use on Gaussian pyramid. Default:"sobel"sigmas (
Optional[Tensor], optional) –coefficients to be multiplied by multichannel response. Should be shape of \((B)\) It is necessary for performing non-maxima-suppression across different scale pyramid levels. See vlfeat. Default:
None
- Return type:
- Returns:
the response map per channel with shape \((B, C, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.tensor([[[ ... [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], ... ]]]) # 1x1x7x7 >>> # compute the response map harris_response(input, 0.04) tensor([[[[0.0012, 0.0039, 0.0020, 0.0000, 0.0020, 0.0039, 0.0012], [0.0039, 0.0065, 0.0040, 0.0000, 0.0040, 0.0065, 0.0039], [0.0020, 0.0040, 0.0029, 0.0000, 0.0029, 0.0040, 0.0020], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0020, 0.0040, 0.0029, 0.0000, 0.0029, 0.0040, 0.0020], [0.0039, 0.0065, 0.0040, 0.0000, 0.0040, 0.0065, 0.0039], [0.0012, 0.0039, 0.0020, 0.0000, 0.0020, 0.0039, 0.0012]]]])
- kornia.feature.hessian_response(input, grads_mode='sobel', sigmas=None)¶
Compute the absolute of determinant of the Hessian matrix.

Function does not do any normalization or nms. The response map is computed according the following formulation:
\[R = det(H)\]where:
\[\begin{split}M = \sum_{(x,y) \in W} \begin{bmatrix} I_{xx} & I_{xy} \\ I_{xy} & I_{yy} \\ \end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]- Parameters:
input (
Tensor) – input image with shape \((B, C, H, W)\).grads_mode (
str, optional) – can be'sobel'for standalone use or'diff'for use on Gaussian pyramid. Default:"sobel"sigmas (
Optional[Tensor], optional) –coefficients to be multiplied by multichannel response. Should be shape of \((B)\) It is necessary for performing non-maxima-suppression across different scale pyramid levels. See vlfeat. Default:
None
- Return type:
- Returns:
the response map per channel with shape \((B, C, H, W)\).
- Shape:
Input: \((B, C, H, W)\)
Output: \((B, C, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.tensor([[[ ... [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0.], ... [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], ... ]]]) # 1x1x7x7 >>> # compute the response map hessian_response(input) tensor([[[[0.0155, 0.0334, 0.0194, 0.0000, 0.0194, 0.0334, 0.0155], [0.0334, 0.0575, 0.0339, 0.0000, 0.0339, 0.0575, 0.0334], [0.0194, 0.0339, 0.0497, 0.0000, 0.0497, 0.0339, 0.0194], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0194, 0.0339, 0.0497, 0.0000, 0.0497, 0.0339, 0.0194], [0.0334, 0.0575, 0.0339, 0.0000, 0.0339, 0.0575, 0.0334], [0.0155, 0.0334, 0.0194, 0.0000, 0.0194, 0.0334, 0.0155]]]])
- kornia.feature.dog_response(input)¶
Compute the Difference-of-Gaussian response.
- kornia.feature.dog_response_single(input, sigma1=1.0, sigma2=1.6)¶
Compute the Difference-of-Gaussian response.

- class kornia.feature.BlobHessian(grads_mode='sobel')¶
Module that calculates Hessian blobs.

See
hessian_response()for details.
- class kornia.feature.CornerGFTT(grads_mode='sobel')¶
Module that calculates Shi-Tomasi corners.

See
gftt_response()for details.
- class kornia.feature.CornerHarris(k, grads_mode='sobel')¶
Module that calculates Harris corners.

See
harris_response()for details.
- class kornia.feature.BlobDoG¶
Module that calculates Difference-of-Gaussians blobs.
See :func: ~kornia.feature.dog_response for details.
- class kornia.feature.BlobDoGSingle(sigma1=1.0, sigma2=1.6)¶
Module that calculates Difference-of-Gaussians blobs.

See
dog_response_single()for details.
- class kornia.feature.KeyNet(pretrained=False, keynet_conf=keynet_default_config)¶
Key.Net model definition – local feature detector (response function). This is based on the original code from paper “Key.Net: Keypoint Detection by Handcrafted and Learned CNN Filters”. See [BLRPM19] for more details.

- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:Falsekeynet_conf (
KeyNet_conf, optional) – Dict with initialization parameters. Do not pass it, unless you know what you are doing`. Default:keynet_default_config
- Returns:
KeyNet response score.
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, H, W)\)
Output: \((B, 1, H, W)\)
- class kornia.feature.MultiResolutionDetector(model, num_features=2048, config=get_default_detector_config(), ori_module=None, aff_module=None)¶
Multi-scale feature detector, based on code from KeyNet. Can be used with any response function.
This is based on the original code from paper “Key.Net: Keypoint Detection by Handcrafted and Learned CNN Filters”. See [BLRPM19] for more details.
- Parameters:
model (
Module) – response function, such as KeyNet or BlobHessiannum_features (
int, optional) – Number of features to detect. Default:2048conf – Dict with initialization parameters. Do not pass it, unless you know what you are doing`.
ori_module (
Optional[Module], optional) – for local feature orientation estimation. Default:PassLAF, which does nothing. SeeLAFOrienterfor details.aff_module (
Optional[Module], optional) – for local feature affine shape estimation. Default:PassLAF, which does nothing. SeeLAFAffineShapeEstimatorfor details.
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
Three stage local feature detection. First the location and scale of interest points are determined by detect function. Then affine shape and orientation.
- Parameters:
img (
Tensor) – image to extract features with shape [1xCxHxW]. KeyNetDetector does not support batch processing,
- because the number of detections is different on each image.
- mask: a mask with weights where to apply the response function. The shape must be the same as
the input image.
- Returns:
shape [1xNx2x3]. Detected local affine frames. responses: shape [1xNx1]. Response function values for corresponding lafs
- Return type:
lafs
- class kornia.feature.ScaleSpaceDetector(num_features=500, mr_size=6.0, scale_pyr_module=ScalePyramid(3, 1.6, 15), resp_module=BlobHessian(), nms_module=ConvSoftArgmax3d((3, 3, 3), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), normalized_coordinates=False, output_value=True), ori_module=PassLAF(), aff_module=PassLAF(), minima_are_also_good=False, scale_space_response=False)¶
Module for differentiable local feature detection, as close as possible to classical local feature detectors like Harris, Hessian-Affine or SIFT (DoG).
It has 5 modules inside: scale pyramid generator, response (“cornerness”) function, soft nms function, affine shape estimator and patch orientation estimator. Each of those modules could be replaced with learned custom one, as long, as they respect output shape.
- Parameters:
num_features (
int, optional) – Number of features to detect. In order to keep everything batchable, output would always have num_features output, even for completely homogeneous images. Default:500mr_size (
float, optional) – multiplier for local feature scale compared to the detection scale. 6.0 is matching OpenCV 12.0 convention for SIFT. Default:6.0scale_pyr_module (
Module, optional) – generates scale pyramid. SeeScalePyramidfor details. Default: ScalePyramid(3, 1.6, 10).resp_module (
Module, optional) – calculates'cornerness'of the pixel. Default:BlobHessian()nms_module (
Module, optional) – outputs per-patch coordinates of the response maxima. SeeConvSoftArgmax3dfor details. Default:ConvSoftArgmax3d((3, 3, 3), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), normalized_coordinates=False, output_value=True)ori_module (
Module, optional) – for local feature orientation estimation. Default:class:~kornia.feature.PassLAF, which does nothing. SeeLAFOrienterfor details. Default:PassLAF()aff_module (
Module, optional) – for local feature affine shape estimation. Default:PassLAF, which does nothing. SeeLAFAffineShapeEstimatorfor details.minima_are_also_good (
bool, optional) – if True, then both response function minima and maxima are detected Useful for symmetric response functions like DoG or Hessian. Default is False Default:False
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
Three stage local feature detection. First the location and scale of interest points are determined by detect function. Then affine shape and orientation.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
shape [BxNx2x3]. Detected local affine frames. responses: shape [BxNx1]. Response function values for corresponding lafs
- Return type:
lafs
- class kornia.feature.KeyNetDetector(pretrained=False, num_features=2048, keynet_conf=keynet_default_config, ori_module=None, aff_module=None)¶
Multi-scale feature detector based on KeyNet.
This is based on the original code from paper “Key.Net: Keypoint Detection by Handcrafted and Learned CNN Filters”. See [BLRPM19] for more details.
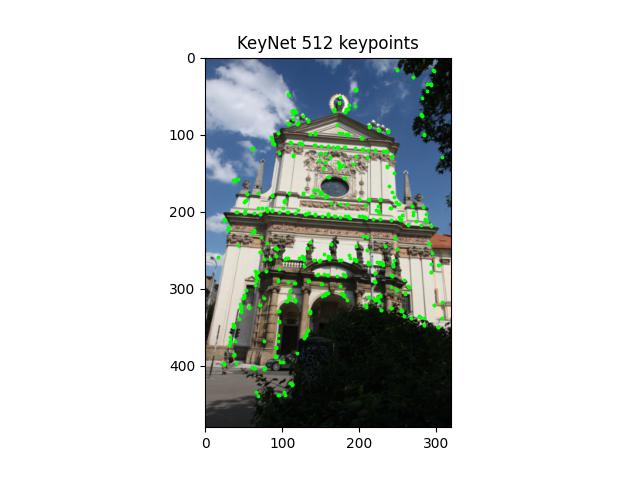
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:Falsenum_features (
int, optional) – Number of features to detect. Default:2048keynet_conf (
KeyNet_conf, optional) – Dict with initialization parameters. Do not pass it, unless you know what you are doing`. Default:keynet_default_configori_module (
Optional[Module], optional) – for local feature orientation estimation. Default:PassLAF, which does nothing. SeeLAFOrienterfor details.aff_module (
Optional[Module], optional) – for local feature affine shape estimation. Default:PassLAF, which does nothing. SeeLAFAffineShapeEstimatorfor details.
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
Three stage local feature detection. First the location and scale of interest points are determined by detect function. Then affine shape and orientation.
- Parameters:
img (
Tensor) – image to extract features with shape [1xCxHxW]. KeyNetDetector does not support batch processing,
- because the number of detections is different on each image.
- mask: a mask with weights where to apply the response function. The shape must be the same as
the input image.
- Returns:
shape [1xNx2x3]. Detected local affine frames. responses: shape [1xNx1]. Response function values for corresponding lafs
- Return type:
lafs
Descriptors¶
- class kornia.feature.DenseSIFTDescriptor(num_ang_bins=8, num_spatial_bins=4, spatial_bin_size=4, rootsift=True, clipval=0.2, stride=1, padding=1)¶
Module, which computes SIFT descriptor densely over the image.
- Parameters:
- You might want to set odd number and relevant padding to keep feature map size
spatial_bin_size: Size of a spatial bin in pixels (4 is default) clipval: clipping value to reduce single-bin dominance rootsift: (bool) if True, RootSIFT (Arandjelović et. al, 2012) is computed stride: default 1 padding: default 0
- Returns:
DenseSIFT descriptor of the image
- Return type:
Tensor
- Shape:
Input: (B, 1, H, W)
Output: (B, num_ang_bins * num_spatial_bins ** 2, (H+padding)/stride, (W+padding)/stride)
- Examples::
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 1, 200, 300) >>> SIFT = DenseSIFTDescriptor() >>> descs = SIFT(input) # 2x128x194x294
- class kornia.feature.SIFTDescriptor(patch_size=41, num_ang_bins=8, num_spatial_bins=4, rootsift=True, clipval=0.2)¶
Module which computes SIFT descriptors of given patches.
- Parameters:
patch_size (
int, optional) – Input patch size in pixels. Default:41num_ang_bins (
int, optional) – Number of angular bins. Default:8num_spatial_bins (
int, optional) – Number of spatial bins. Default:4clipval (
float, optional) – clipping value to reduce single-bin dominance Default:0.2rootsift (
bool, optional) – ifTrue, RootSIFT (Arandjelović et. al, 2012) is computed. Default:True
- Returns:
SIFT descriptor of the patches with shape.
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, \text{num_spatial_bins}, \text{num_spatial_bins})\)
Output: \((B, \text{num_ang_bins * num_spatial_bins ** 2})\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(23, 1, 32, 32) >>> SIFT = SIFTDescriptor(32, 8, 4) >>> descs = SIFT(input) # 23x128
- class kornia.feature.MKDDescriptor(patch_size=32, kernel_type='concat', whitening='pcawt', training_set='liberty', output_dims=128)¶
Module that computes Multiple Kernel local descriptors.
This is based on the paper “Understanding and Improving Kernel Local Descriptors”. See [MTB+19] for more details.
- Parameters:
patch_size (
int, optional) – Input patch size in pixels. Default:32kernel_type (
str, optional) – Parametrization of kernel'concat','cart','polar'. Default:"concat"whitening (
str, optional) – Whitening transform to applyNone,'lw','pca','pcawt','pcaws'. Default:"pcawt"training_set (
str, optional) – Set that model was trained on'liberty','notredame','yosemite'. Default:"liberty"output_dims (
int, optional) – Dimensionality reduction. Default:128
- Returns:
Explicit cartesian or polar embedding.
- Shape:
Input: \((B, in_{dims}, fmap_{size}, fmap_{size})\).
Output: \((B, out_{dims}, fmap_{size}, fmap_{size})\),
Examples
>>> patches = torch.rand(23, 1, 32, 32) >>> mkd = MKDDescriptor(patch_size=32, ... kernel_type='concat', ... whitening='pcawt', ... training_set='liberty', ... output_dims=128) >>> desc = mkd(patches) # 23x128
- class kornia.feature.HardNet(pretrained=False)¶
Module, which computes HardNet descriptors of given grayscale patches of 32x32.
This is based on the original code from paper “Working hard to know your neighbor’s margins: Local descriptor learning loss”. See [MMRM17] for more details.
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:False- Returns:
HardNet descriptor of the patches.
- Return type:
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, 32, 32)\)
Output: \((B, 128)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(16, 1, 32, 32) >>> hardnet = HardNet() >>> descs = hardnet(input) # 16x128
- class kornia.feature.HardNet8(pretrained=False)¶
Module, which computes HardNet8 descriptors of given grayscale patches of 32x32.
This is based on the original code from paper “Improving the HardNet Descriptor”. See [Pul20] for more details.
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:False- Returns:
HardNet8 descriptor of the patches.
- Return type:
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, 32, 32)\)
Output: \((B, 128)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(16, 1, 32, 32) >>> hardnet = HardNet8() >>> descs = hardnet(input) # 16x128
- class kornia.feature.HyNet(pretrained=False, is_bias=True, is_bias_FRN=True, dim_desc=128, drop_rate=0.3, eps_l2_norm=1e-10)¶
Module, which computes HyNet descriptors of given grayscale patches of 32x32.
This is based on the original code from paper “HyNet: Learning Local Descriptor with Hybrid Similarity Measure and Triplet Loss”. See [TBLN+20] for more details.
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:Falseis_bias (
bool, optional) – use bias in TLU layers Default:Trueis_bias_FRN (
bool, optional) – use bias in FRN layers Default:Truedim_desc (
int, optional) – descriptor dimensionality, Default:128drop_rate (
float, optional) – dropout rate, Default:0.3eps_l2_norm (
float, optional) – to avoid div by zero Default:1e-10
- Returns:
HyNet descriptor of the patches.
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, 32, 32)\)
Output: \((B, 128)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(16, 1, 32, 32) >>> hynet = HyNet() >>> descs = hynet(input) # 16x128
- class kornia.feature.TFeat(pretrained=False)¶
Module, which computes TFeat descriptors of given grayscale patches of 32x32.
This is based on the original code from paper “Learning local feature descriptors with triplets and shallow convolutional neural networks”. See [BRPM16] for more details
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:False- Returns:
TFeat descriptor of the patches.
- Return type:
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, 32, 32)\)
Output: \((B, 128)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(16, 1, 32, 32) >>> tfeat = TFeat() >>> descs = tfeat(input) # 16x128
- class kornia.feature.SOSNet(pretrained=False)¶
128-dimensional SOSNet model definition for 32x32 patches.
This is based on the original code from paper “SOSNet:Second Order Similarity Regularization for Local Descriptor Learning”.
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:False
- Shape:
Input: \((B, 1, 32, 32)\)
Output: \((B, 128)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(8, 1, 32, 32) >>> sosnet = SOSNet() >>> descs = sosnet(input) # 8x128
- class kornia.feature.LAFDescriptor(patch_descriptor_module=None, patch_size=32, grayscale_descriptor=True)¶
Module to get local descriptors, corresponding to LAFs (keypoints).
Internally uses
get_laf_descriptors().- Parameters:
patch_descriptor_module (
Optional[Module], optional) – patch descriptor module, e.g.SIFTDescriptororHardNet. Default:HardNet.patch_size (
int, optional) – patch size in pixels, which descriptor expects. Default:32grayscale_descriptor (
bool, optional) –Trueif patch_descriptor expects single-channel image. Default:True
- forward(img, lafs)¶
Three stage local feature detection.
First the location and scale of interest points are determined by detect function. Then affine shape and orientation.
- class kornia.feature.SOLD2(pretrained=True, config=None)¶
Module, which detects and describe line segments in an image.
This is based on the original code from the paper “SOLD²: Self-supervised Occlusion-aware Line Detector and Descriptor”. See [PautratLinL+21] for more details.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The raw junction and line heatmaps, the semi-dense descriptor map, as well as the list of detected line segments (ij coordinates convention).
Example
>>> images = torch.rand(2, 1, 512, 512) >>> sold2 = SOLD2() >>> outputs = sold2(images) >>> line_seg1 = outputs["line_segments"][0] >>> line_seg2 = outputs["line_segments"][1] >>> desc1 = outputs["dense_desc"][0] >>> desc2 = outputs["dense_desc"][1] >>> matches = sold2.match(line_seg1, line_seg2, desc1[None], desc2[None])
- forward(img)¶
- Parameters:
img (
Tensor) – batched images with shape \((B, 1, H, W)\).- Returns:
list of N line segments in each of the B images \(List[(N, 2, 2)]\). -
junction_heatmap: raw junction heatmap of shape \((B, H, W)\). -line_heatmap: raw line heatmap of shape \((B, H, W)\). -dense_desc: the semi-dense descriptor map of shape \((B, 128, H/4, W/4)\).- Return type:
line_segments
- kornia.feature.get_laf_descriptors(img, lafs, patch_descriptor, patch_size=32, grayscale_descriptor=True)¶
Function to get local descriptors, corresponding to LAFs (keypoints).
- Parameters:
img (
Tensor) – image features with shape \((B,C,H,W)\).lafs (
Tensor) – local affine frames \((B,N,2,3)\).patch_descriptor (
Module) – patch descriptor module, e.g.SIFTDescriptororHardNet.patch_size (
int, optional) – patch size in pixels, which descriptor expects. Default:32grayscale_descriptor (
bool, optional) – True ifpatch_descriptorexpects single-channel image. Default:True
- Return type:
- Returns:
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
Local Features (Detector and Descriptors together)¶
- class kornia.feature.LocalFeature(detector, descriptor, scaling_coef=1.0)¶
Module, which combines local feature detector and descriptor.
- Parameters:
detector (
Module) – the detection module.descriptor (
LAFDescriptor) – the descriptor module.scaling_coef (
float, optional) – multiplier for change default detector scale (e.g. it is too small for KeyNet by default) Default:1.0
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Detected local affine frames with shape \((B,N,2,3)\).
Response function values for corresponding lafs with shape \((B,N,1)\).
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
- class kornia.feature.SOLD2_detector(pretrained=True, config=None)¶
Module, which detects line segments in an image.
This is based on the original code from the paper “SOLD²: Self-supervised Occlusion-aware Line Detector and Descriptor”. See [PautratLinL+21] for more details.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The raw junction and line heatmaps, as well as the list of detected line segments (ij coordinates convention).
Example
>>> img = torch.rand(1, 1, 512, 512) >>> sold2_detector = SOLD2_detector() >>> line_segments = sold2_detector(img)["line_segments"]
- forward(img)¶
- Parameters:
img (
Tensor) – batched images with shape \((B, 1, H, W)\).- Returns:
list of N line segments in each of the B images \(List[(N, 2, 2)]\). -
junction_heatmap: raw junction heatmap of shape \((B, H, W)\). -line_heatmap: raw line heatmap of shape \((B, H, W)\).- Return type:
line_segments
- class kornia.feature.DeDoDe(detector_model='L', descriptor_model='G', amp_dtype=torch.float16)¶
Module which detects and/or describes local features in an image using the DeDode method.
See [EBWF24] for details.
Note
DeDode takes ImageNet normalized images as input (not in range [0, 1]).
- Parameters:
detector_model (
Literal['L'], optional) – The detector model kind. Available options are: L. Default:"L"descriptor_model (
Literal['G','B'], optional) – The descriptor model kind. Available options are: G or B Default:"G"amp_dtype (
dtype, optional) – The automatic mixed precision desired. Default:torch.float16
Example
>>> dedode = DeDoDe.from_pretrained(detector_weights="L-C4-v2", descriptor_weights="B-upright") >>> images = torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256) >>> keypoints, scores = dedode.detect(images) >>> descriptions = dedode.describe(images, keypoints = keypoints) >>> keypoints, scores, features = dedode(images) # alternatively do both
- describe(images, keypoints=None, apply_imagenet_normalization=True)¶
Describes keypoints in the input images. If keypoints are not provided, returns the dense descriptors.
- Parameters:
images (
Tensor) – A tensor of shape \((B, 3, H, W)\) containing the input images.keypoints (
Optional[Tensor], optional) – An optional tensor of shape \((B, N, 2)\) containing the detected keypoints. Default:Noneapply_imagenet_normalization (
bool, optional) – Whether to apply ImageNet normalization to the input images. Default:True
- Returns:
A tensor of shape \((B, N, DIM)\) containing the descriptions of the detected keypoints. If the dense descriptors are requested, the shape is \((B, DIM, H, W)\).
- Return type:
descriptions
- detect(images, n=10000, apply_imagenet_normalization=True, pad_if_not_divisible=True, crop_h=None, crop_w=None)¶
Detects keypoints in the input images.
- Parameters:
images (
Tensor) – A tensor of shape \((B, 3, H, W)\) containing the input images.n (
Optional[int], optional) – The number of keypoints to detect. Default:10000apply_imagenet_normalization (
bool, optional) – Whether to apply ImageNet normalization to the input images. Default:Truecrop_h (
Optional[int], optional) – The height of the crop to be used for detection. If None, the full image is used. Default:Nonecrop_w (
Optional[int], optional) – The width of the crop to be used for detection. If None, the full image is used. Default:None
- Returns:
A tensor of shape \((B, N, 2)\) containing the detected keypoints, normalized to the range \([-1, 1]\). scores: A tensor of shape \((B, N)\) containing the scores of the detected keypoints.
- Return type:
keypoints
- forward(images, n=10_000, apply_imagenet_normalization=True, pad_if_not_divisible=True)¶
Detects and describes keypoints in the input images.
- Parameters:
images (
Tensor) – A tensor of shape \((B, 3, H, W)\) containing the ImageNet-Normalized input images.n (
Optional[int], optional) – The number of keypoints to detect. Default:10_000apply_imagenet_normalization (
bool, optional) – Whether to apply ImageNet normalization to the input images. Default:True
- Returns:
A tensor of shape \((B, N, 2)\) containing the detected keypoints in the image range, unlike .detect() function scores: A tensor of shape \((B, N)\) containing the scores of the detected keypoints. descriptions: A tensor of shape \((B, N, DIM)\) containing the descriptions of the detected keypoints. DIM is 256 for B and 512 for G.
- Return type:
keypoints
- classmethod from_pretrained(detector_weights='L-C4-v2', descriptor_weights='G-upright', amp_dtype=torch.float16)¶
Loads a pretrained model.
- Parameters:
detector_weights (
str, optional) – The weights to load for the detector. One of ‘L-upright’ (original paper, https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.08479), ‘L-C4’, ‘L-SO2’ (from steerers, better for rotations, https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.02152), ‘L-C4-v2’ (from dedode v2, better at rotations, less clustering, https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.08928) Default is ‘L-C4-v2’, but perhaps it should be ‘L-C4-v2’? Default:"L-C4-v2"descriptor_weights (
str, optional) – The weights to load for the descriptor. One of ‘B-upright’,’G-upright’ (original paper, https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.08479), ‘B-C4’, ‘B-SO2’, ‘G-C4’ (from steerers, better for rotations, https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.02152). Default is ‘G-upright’. Default:"G-upright"amp_dtype (
dtype, optional) – the dtype to use for the model. One of torch.float16 or torch.float32. Default:torch.float16torch.float16 (Default is)
MPS (suitable for CUDA. Use torch.float32 for CPU or)
- Return type:
- Returns:
The pretrained model.
- class kornia.feature.DISK(desc_dim=128, unet=None)¶
Module which detects and described local features in an image using the DISK method. See [TFT20] for details.
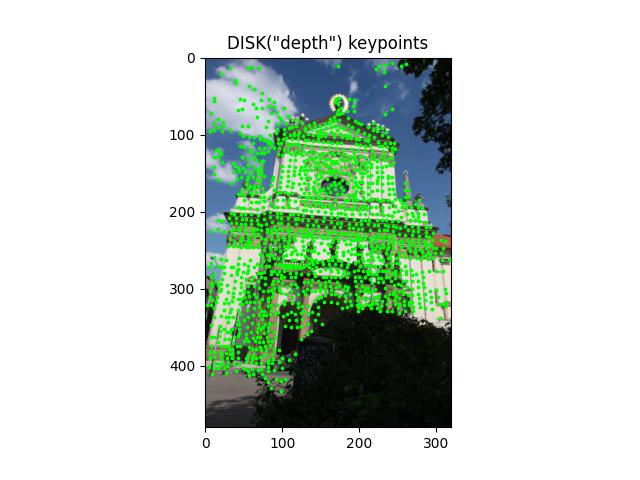
- Parameters:
desc_dim (
int, optional) – The dimension of the descriptor. Default:128unet (
None|Module, optional) – The U-Net to use. If None, a default U-Net is used. Kornia doesn’t provide the training code for DISK so this is only useful when using a custom checkpoint trained using the code released with the paper. The unet should take as input a tensor of shape \((B, C, H, W)\) and output a tensor of shape \((B, \mathrm{desc\_dim} + 1, H, W)\). Default:None
Example
>>> disk = DISK.from_pretrained('depth') >>> images = torch.rand(1, 3, 256, 256) >>> features = disk(images)
- forward(images, n=None, window_size=5, score_threshold=0.0, pad_if_not_divisible=False)¶
Detects features in an image, returning keypoint locations, descriptors and detection scores.
- Parameters:
images (
Tensor) – The image to detect features in. Shape \((B, 3, H, W)\).n (
Optional[int], optional) – The maximum number of keypoints to detect. If None, all keypoints are returned. Default:Nonewindow_size (
int, optional) – The size of the non-maxima suppression window used to filter detections. Default:5score_threshold (
float, optional) – The minimum score a detection must have to be returned. SeeDISKFeaturesfor details. Default:0.0pad_if_not_divisible (
bool, optional) – if True, the non-16 divisible input is zero-padded to the closest 16-multiply Default:False
- Return type:
- Returns:
A list of length \(B\) containing the detected features.
- classmethod from_pretrained(checkpoint='depth', device=torch.device('cpu'))¶
Loads a pretrained model.
Depth model was trained using depth map supervision and is slightly more precise but biased to detect keypoints only where SfM depth is available. Epipolar model was trained using epipolar geometry supervision and is less precise but detects keypoints everywhere where they are matchable. The difference is especially pronounced on thin structures and on edges of objects.
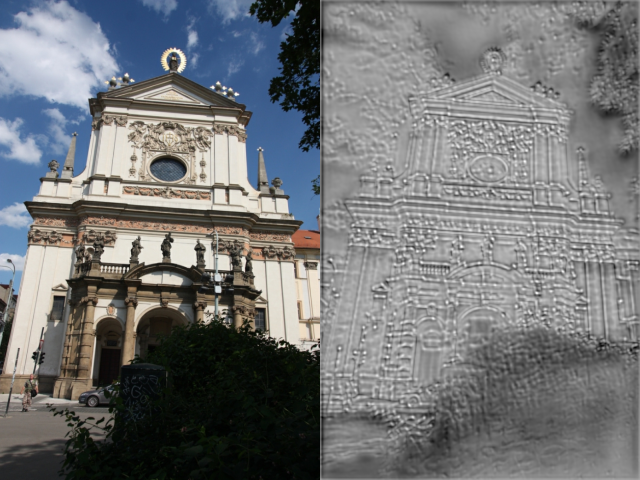
- heatmap_and_dense_descriptors(images)¶
Returns the heatmap and the dense descriptors.

- class kornia.feature.DISKFeatures(keypoints, descriptors, detection_scores)¶
A data structure holding DISK keypoints, descriptors and detection scores for an image. Since DISK detects a varying number of keypoints per image, DISKFeatures is not batched.
- Parameters:
keypoints (
Tensor) – Tensor of shape \((N, 2)\), where \(N\) is the number of keypoints.descriptors (
Tensor) – Tensor of shape \((N, D)\), where \(D\) is the descriptor dimension.detection_scores (
Tensor) – Tensor of shape \((N,)\) where the detection score can be interpreted as the log-probability of keeping a keypoint after it has been proposed (see the paper section Method → Feature distribution for details).
- to(*args, **kwargs)¶
Calls
torch.Tensor.to()on each tensor to move the keypoints, descriptors and detection scores to the specified device and/or data type.- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
A new DISKFeatures object with tensors of appropriate type and location.
- class kornia.feature.SIFTFeature(num_features=8000, upright=False, rootsift=True, device=torch.device('cpu'), config=get_default_detector_config())¶
Convenience module, which implements DoG detector + (Root)SIFT descriptor.
Using kornia.feature.MultiResolutionDetector without blur pyramid Still not as good as OpenCV/VLFeat because of https://github.com/kornia/kornia/pull/884, but we are working on it
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Detected local affine frames with shape \((B,N,2,3)\).
Response function values for corresponding lafs with shape \((B,N,1)\).
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
- class kornia.feature.SIFTFeatureScaleSpace(num_features=8000, upright=False, rootsift=True, device=torch.device('cpu'))¶
Convenience module, which implements DoG detector + (Root)SIFT descriptor. Using kornia.feature.ScaleSpaceDetector with blur pyramid.
Still not as good as OpenCV/VLFeat because of https://github.com/kornia/kornia/pull/884, but we are working on it
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Detected local affine frames with shape \((B,N,2,3)\).
Response function values for corresponding lafs with shape \((B,N,1)\).
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
- class kornia.feature.GFTTAffNetHardNet(num_features=8000, upright=False, device=torch.device('cpu'), config=get_default_detector_config())¶
Convenience module, which implements GFTT detector + AffNet-HardNet descriptor.
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Detected local affine frames with shape \((B,N,2,3)\).
Response function values for corresponding lafs with shape \((B,N,1)\).
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
- class kornia.feature.KeyNetAffNetHardNet(num_features=8000, upright=False, device=torch.device('cpu'), scale_laf=1.0)¶
Convenience module, which implements KeyNet detector + AffNet + HardNet descriptor.
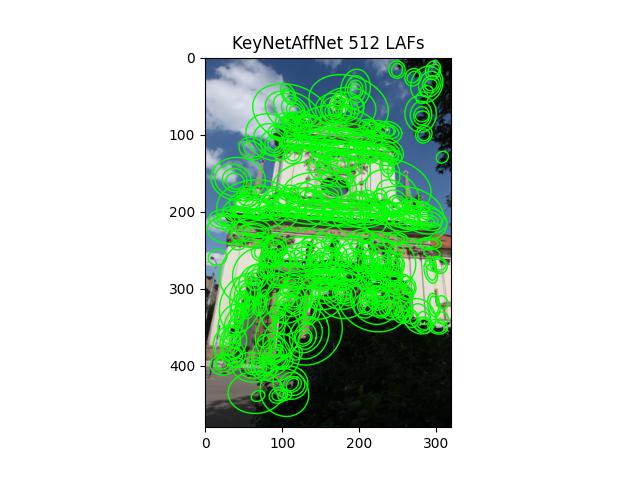
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Detected local affine frames with shape \((B,N,2,3)\).
Response function values for corresponding lafs with shape \((B,N,1)\).
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
- class kornia.feature.KeyNetHardNet(num_features=8000, upright=False, device=torch.device('cpu'), scale_laf=1.0)¶
Convenience module, which implements KeyNet detector + HardNet descriptor.
- forward(img, mask=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Detected local affine frames with shape \((B,N,2,3)\).
Response function values for corresponding lafs with shape \((B,N,1)\).
Local descriptors of shape \((B,N,D)\) where \(D\) is descriptor size.
Matching¶
- kornia.feature.match_nn(desc1, desc2, dm=None)¶
Function, which finds nearest neighbors in desc2 for each vector in desc1.
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B1, 1)\).
Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2, shape of \((B1, 2)\).
- kornia.feature.match_mnn(desc1, desc2, dm=None)¶
Function, which finds mutual nearest neighbors in desc2 for each vector in desc1.
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of. \((B3, 1)\).
Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2, shape of \((B3, 2)\), where 0 <= B3 <= min(B1, B2)
- kornia.feature.match_snn(desc1, desc2, th=0.8, dm=None)¶
Function, which finds nearest neighbors in desc2 for each vector in desc1.
The method satisfies first to second nearest neighbor distance <= th.
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
desc1 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B1, D)\).desc2 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B2, D)\).th (
float, optional) – distance ratio threshold. Default:0.8dm (
Optional[Tensor], optional) – Tensor containing the distances from each descriptor in desc1 to each descriptor in desc2, shape of \((B1, B2)\). Default:None
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B3, 1)\).
Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2. Shape: \((B3, 2)\), where 0 <= B3 <= B1.
- kornia.feature.match_smnn(desc1, desc2, th=0.95, dm=None)¶
Function, which finds mutual nearest neighbors in desc2 for each vector in desc1.
the method satisfies first to second nearest neighbor distance <= th.
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
desc1 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B1, D)\).desc2 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B2, D)\).th (
float, optional) – distance ratio threshold. Default:0.95dm (
Optional[Tensor], optional) – Tensor containing the distances from each descriptor in desc1 to each descriptor in desc2, shape of \((B1, B2)\). Default:None
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of. \((B3, 1)\).
Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2, shape of \((B3, 2)\) where 0 <= B3 <= B1.
- kornia.feature.match_fginn(desc1, desc2, lafs1, lafs2, th=0.8, spatial_th=10.0, mutual=False, dm=None)¶
Function, which finds nearest neighbors in desc2 for each vector in desc1.
The method satisfies first to second nearest neighbor distance <= th, and assures 2nd nearest neighbor is geometrically inconsistent with the 1st one (see [MMP15] for more details)
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
desc1 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B1, D)\).desc2 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B2, D)\).lafs1 (
Tensor) – LAFs of a shape \((1, B1, 2, 3)\).lafs2 (
Tensor) – LAFs of a shape \((1, B2, 2, 3)\).th (
float, optional) – distance ratio threshold. Default:0.8spatial_th (
float, optional) – minimal distance in pixels to 2nd nearest neighbor. Default:10.0mutual (
bool, optional) – also perform mutual nearest neighbor check Default:Falsedm (
Optional[Tensor], optional) – Tensor containing the distances from each descriptor in desc1 to each descriptor in desc2, shape of \((B1, B2)\). Default:None
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B3, 1)\).
Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2. Shape: \((B3, 2)\), where 0 <= B3 <= B1.
- kornia.feature.match_adalam(desc1, desc2, lafs1, lafs2, config=None, hw1=None, hw2=None, dm=None)¶
Function, which performs descriptor matching, followed by AdaLAM filtering (see [CLO+20] for more details)
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
desc1 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B1, D)\).desc2 (
Tensor) – Batch of descriptors of a shape \((B2, D)\).lafs1 (
Tensor) – LAFs of a shape \((1, B1, 2, 3)\).lafs2 (
Tensor) – LAFs of a shape \((1, B2, 2, 3)\).config (
Optional[AdalamConfig], optional) – dict with AdaLAM config Default:Nonedm (
Optional[Tensor], optional) – Tensor containing the distances from each descriptor in desc1 to each descriptor in desc2, shape of \((B1, B2)\). Default:None
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B3, 1)\).
Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2. Shape: \((B3, 2)\), where 0 <= B3 <= B1.
- class kornia.feature.DescriptorMatcher(match_mode='snn', th=0.8)¶
Module version of matching functions.
- See
match_nn(),match_snn(), match_mnn()ormatch_smnn()for more details.
- Parameters:
- forward(desc1, desc2)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B3, 1)\).
- Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2,
shape of \((B3, 2)\) where \(0 <= B3 <= B1\).
- See
- class kornia.feature.GeometryAwareDescriptorMatcher(match_mode='fginn', params={})¶
Module version of matching functions.
- See
match_nn(),match_snn(), match_mnn()ormatch_smnn()for more details.
- Parameters:
match_mode (
str, optional) – type of matching, can be fginn. Default:"fginn"th – threshold on distance ratio, or other quality measure.
- forward(desc1, desc2, lafs1, lafs2)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B3, 1)\).
- Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2,
shape of \((B3, 2)\) where \(0 <= B3 <= B1\).
- See
- class kornia.feature.LocalFeatureMatcher(local_feature, matcher)¶
Module, which finds correspondences between two images based on local features.
- Parameters:
local_feature (
Module) – Local feature detector. SeeGFTTAffNetHardNet.matcher (
Module) – Descriptor matcher, seeDescriptorMatcher.
- Returns:
Dictionary with image correspondences and confidence scores.
- Return type:
Dict[str, Tensor]
Example
>>> img1 = torch.rand(1, 1, 320, 200) >>> img2 = torch.rand(1, 1, 128, 128) >>> input = {"image0": img1, "image1": img2} >>> gftt_hardnet_matcher = LocalFeatureMatcher( ... GFTTAffNetHardNet(10), kornia.feature.DescriptorMatcher('snn', 0.8) ... ) >>> out = gftt_hardnet_matcher(input)
- forward(data)¶
- Parameters:
data (
Dict[str,Tensor]) – dictionary containing the input data in the following format:- Keyword Arguments:
image0 – left image with shape \((N, 1, H1, W1)\).
image1 – right image with shape \((N, 1, H2, W2)\).
mask0 (optional) – left image mask. ‘0’ indicates a padded position \((N, H1, W1)\).
mask1 (optional) – right image mask. ‘0’ indicates a padded position \((N, H2, W2)\).
- Return type:
- Returns:
keypoints0, matching keypoints from image0 \((NC, 2)\).keypoints1, matching keypoints from image1 \((NC, 2)\).confidence, confidence score [0, 1] \((NC)\).lafs0, matching LAFs from image0 \((1, NC, 2, 3)\).lafs1, matching LAFs from image1 \((1, NC, 2, 3)\).batch_indexes, batch indexes for the keypoints and lafs \((NC)\).
- class kornia.feature.LightGlueMatcher(feature_name='disk', params={})¶
LightGlue-based matcher in kornia API.
This is based on the original code from paper “LightGlue: Local Feature Matching at Light Speed”. See [LSP23] for more details.
- Parameters:
- forward(desc1, desc2, lafs1, lafs2, hw1=None, hw2=None)¶
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Descriptor distance of matching descriptors, shape of \((B3, 1)\).
- Long tensor indexes of matching descriptors in desc1 and desc2,
shape of \((B3, 2)\) where \(0 <= B3 <= B1\).
- class kornia.feature.LightGlue(features='superpoint', **conf_)¶
- forward(data)¶
Match keypoints and descriptors between two images.
- Return type:
- Input (dict):
- image0: dict
keypoints: [B x M x 2] descriptors: [B x M x D] image: [B x C x H x W] or image_size: [B x 2]
- image1: dict
keypoints: [B x N x 2] descriptors: [B x N x D] image: [B x C x H x W] or image_size: [B x 2]
- Output (dict):
log_assignment: [B x M+1 x N+1] matches0: [B x M] matching_scores0: [B x M] matches1: [B x N] matching_scores1: [B x N] matches: List[[Si x 2]], scores: List[[Si]]
- class kornia.feature.LoFTR(pretrained='outdoor', config=default_cfg)¶
Module, which finds correspondences between two images.
This is based on the original code from paper “LoFTR: Detector-Free Local Feature Matching with Transformers”. See [SSW+21] for more details.
If the distance matrix dm is not provided,
torch.cdist()is used.- Parameters:
config (
dict[str,Any], optional) – Dict with initialization parameters. Do not pass it, unless you know what you are doing`. Default:default_cfgpretrained (
Optional[str], optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Options: ‘outdoor’, ‘indoor’. ‘outdoor’ is trained on the MegaDepth dataset and ‘indoor’ on the ScanNet. Default:"outdoor"
- Returns:
Dictionary with image correspondences and confidence scores.
Example
>>> img1 = torch.rand(1, 1, 320, 200) >>> img2 = torch.rand(1, 1, 128, 128) >>> input = {"image0": img1, "image1": img2} >>> loftr = LoFTR('outdoor') >>> out = loftr(input)
- forward(data)¶
- Parameters:
data (
dict[str,Tensor]) – dictionary containing the input data in the following format:- Keyword Arguments:
image0 – left image with shape \((N, 1, H1, W1)\).
image1 – right image with shape \((N, 1, H2, W2)\).
mask0 (optional) – left image mask. ‘0’ indicates a padded position \((N, H1, W1)\).
mask1 (optional) – right image mask. ‘0’ indicates a padded position \((N, H2, W2)\).
- Return type:
- Returns:
keypoints0, matching keypoints from image0 \((NC, 2)\).keypoints1, matching keypoints from image1 \((NC, 2)\).confidence, confidence score [0, 1] \((NC)\).batch_indexes, batch indexes for the keypoints and lafs \((NC)\).
- class kornia.feature.OnnxLightGlue(weights=None, device='cpu')¶
Wrapper for loading LightGlue-ONNX models and running inference via ONNXRuntime.
LightGlue [LSP23] performs fast descriptor-based deep keypoint matching. This module requires onnxruntime to be installed.
If you have trained your own LightGlue model, see https://github.com/fabio-sim/LightGlue-ONNX for how to export the model to ONNX and optimize it.
- Parameters:
weights (
str|None, optional) – Pretrained weights, or a path to your own exported ONNX model. Available pretrained weights are'disk','superpoint','disk_fp16', and'superpoint_fp16'. Note that FP16 requires CUDA. Defaults to'disk_fp16'ifdeviceis CUDA, and'disk'if CPU. Default:Nonedevice (
Union[str,device,None], optional) – Device to run inference on. Default:"cpu"
- forward(data)¶
Match keypoints and descriptors between two images.
The output contains the matches (the indices of the matching keypoint pairs between the first and second image) and the corresponding confidence scores. Only a batch size of 1 is supported.
- Parameters:
data (
dict[str,dict[str,Tensor]]) – Dictionary containing both images and the keypoints and descriptors thereof.- Return type:
- Returns:
Dictionary containing the matches and scores.
data(dict):image0(dict):keypoints(float32): \((1, M, 2)\)descriptors(float32): \((1, M, D)\)image: \((1, C, H, W)\) orimage_size: \((1, 2)\)image1(dict):keypoints(float32): \((1, N, 2)\)descriptors(float32): \((1, N, D)\)image: \((1, C, H, W)\) orimage_size: \((1, 2)\)
output(dict):matches(int64): \((S, 2)\)scores(float32): \((S)\)
Local Affine Frames (LAF)¶
- kornia.feature.extract_patches_from_pyramid(img, laf, PS=32, normalize_lafs_before_extraction=True)¶
Extract patches defined by LAFs from image tensor.
Patches are extracted from appropriate pyramid level.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
patches with shape \((B, N, CH, PS,PS)\).
- kornia.feature.extract_patches_simple(img, laf, PS=32, normalize_lafs_before_extraction=True)¶
Extract patches defined by LAFs from image tensor.
No smoothing applied, huge aliasing (better use extract_patches_from_pyramid).
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
patches with shape \((B, N, CH, PS,PS)\).
- kornia.feature.normalize_laf(LAF, images)¶
Normalize LAFs to [0,1] scale from pixel scale. See below:
B,N,H,W = images.size() MIN_SIZE = min(H - 1, W -1) [a11 a21 x] [a21 a22 y] becomes: [a11/MIN_SIZE a21/MIN_SIZE x/(W-1)] [a21/MIN_SIZE a22/MIN_SIZE y/(H-1)]
- kornia.feature.denormalize_laf(LAF, images)¶
De-normalize LAFs from scale to image scale. The convention is that center of 5-pixel image (coordinates from 0 to 4) is 2, and not 2.5.
B,N,H,W = images.size() MIN_SIZE = min(H - 1, W -1) [a11 a21 x] [a21 a22 y] becomes [a11*MIN_SIZE a21*MIN_SIZE x*(W-1)] [a21*MIN_SIZE a22*MIN_SIZE y*(W-1)]
- kornia.feature.laf_to_boundary_points(LAF, n_pts=50)¶
Convert LAFs to boundary points of the regions + center.
Used for local features visualization, see visualize_laf function.
- kornia.feature.ellipse_to_laf(ells)¶
Convert ellipse regions to LAF format.
Ellipse (a, b, c) and upright covariance matrix [a11 a12; 0 a22] are connected by inverse matrix square root: A = invsqrt([a b; b c]).
See also https://github.com/vlfeat/vlfeat/blob/master/toolbox/sift/vl_frame2oell.m
- Parameters:
ells (
Tensor) – tensor \((B, N, 5)\) of ellipses in Oxford format [x y a b c].- Return type:
- Returns:
LAF \((B, N, 2, 3)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(1, 10, 5) # BxNx5 >>> output = ellipse_to_laf(input) # BxNx2x3
- kornia.feature.make_upright(laf, eps=1e-9)¶
Rectify the affine matrix, so that it becomes upright.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
\((B, N, 2, 3)\)
- Return type:
laf
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(1, 5, 2, 3) # BxNx2x3 >>> output = make_upright(input) # BxNx2x3
- kornia.feature.scale_laf(laf, scale_coef)¶
Multiplies region part of LAF ([:, :, :2, :2]) by a scale_coefficient.
So the center, shape and orientation of the local feature stays the same, but the region area changes.
:param LAF \(: :type LAF :math:\): B, N, 2, 3 :type scale_coef:
Union[float,Tensor] :param scale_coef: broadcastable tensor or float.- Return type:
- Returns:
LAF \((B, N, 2, 3)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(1, 5, 2, 3) # BxNx2x3 >>> scale = 0.5 >>> output = scale_laf(input, scale) # BxNx2x3
- kornia.feature.get_laf_scale(LAF)¶
Return a scale of the LAFs.
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(1, 5, 2, 3) # BxNx2x3 >>> output = get_laf_scale(input) # BxNx1x1
- kornia.feature.get_laf_center(LAF)¶
Return a center (keypoint) of the LAFs. The convention is that center of 5-pixel image (coordinates from 0 to 4) is 2, and not 2.5.
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(1, 5, 2, 3) # BxNx2x3 >>> output = get_laf_center(input) # BxNx2
- kornia.feature.rotate_laf(LAF, angles_degrees)¶
Apply additional rotation to the the LAFs. Compared to set_laf_orientation, the resulting rotation is original LAF orientation plus angles_degrees.
- kornia.feature.get_laf_orientation(LAF)¶
Return orientation of the LAFs, in degrees.
- Parameters:
LAF (
Tensor) – \((B, N, 2, 3)\)- Return type:
- Returns:
angle in degrees \((B, N, 1)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(1, 5, 2, 3) # BxNx2x3 >>> output = get_laf_orientation(input) # BxNx1
- kornia.feature.set_laf_orientation(LAF, angles_degrees)¶
Change the orientation of the LAFs.
- kornia.feature.laf_from_center_scale_ori(xy, scale=None, ori=None)¶
Creates a LAF from keypoint center, scale and orientation.
Useful to create kornia LAFs from OpenCV keypoints.
- kornia.feature.laf_is_inside_image(laf, images, border=0)¶
Check if the LAF is touching or partly outside the image boundary.
Returns the mask of LAFs, which are fully inside the image, i.e. valid.
- kornia.feature.laf_to_three_points(laf)¶
Convert local affine frame(LAF) to alternative representation: coordinates of LAF center, LAF-x unit vector, LAF-y unit vector.
- kornia.feature.laf_from_three_points(threepts)¶
Convert three points to local affine frame.
Order is (0,0), (0, 1), (1, 0).
- kornia.feature.KORNIA_CHECK_LAF(laf, raises=True)¶
Check whether a Local Affine Frame (laf) has a valid shape.
- Parameters:
- Raises:
Exception – if the input laf does not have a shape \((B,N,2,3)\) and raises is True.
- Return type:
Example
>>> lafs = torch.rand(2, 10, 2, 3) >>> KORNIA_CHECK_LAF(lafs) True
- kornia.feature.perspective_transform_lafs(trans_01, lafs_1)¶
Function that applies perspective transformations to a set of local affine frames (LAFs).
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
tensor of N-dimensional points of shape \((B, N, 2, 3)\).
Examples
>>> rng = torch.manual_seed(0) >>> lafs_1 = torch.rand(2, 4, 2, 3) # BxNx2x3 >>> lafs_1 tensor([[[[0.4963, 0.7682, 0.0885], [0.1320, 0.3074, 0.6341]], [[0.4901, 0.8964, 0.4556], [0.6323, 0.3489, 0.4017]], [[0.0223, 0.1689, 0.2939], [0.5185, 0.6977, 0.8000]], [[0.1610, 0.2823, 0.6816], [0.9152, 0.3971, 0.8742]]], [[[0.4194, 0.5529, 0.9527], [0.0362, 0.1852, 0.3734]], [[0.3051, 0.9320, 0.1759], [0.2698, 0.1507, 0.0317]], [[0.2081, 0.9298, 0.7231], [0.7423, 0.5263, 0.2437]], [[0.5846, 0.0332, 0.1387], [0.2422, 0.8155, 0.7932]]]]) >>> trans_01 = torch.eye(3).repeat(2, 1, 1) # Bx3x3 >>> trans_01.shape torch.Size([2, 3, 3]) >>> lafs_0 = perspective_transform_lafs(trans_01, lafs_1) # BxNx2x3
- class kornia.feature.PassLAF(*args, **kwargs)¶
Dummy module to use instead of local feature orientation or affine shape estimator.
- class kornia.feature.PatchAffineShapeEstimator(patch_size=19, eps=1e-10)¶
Module, which estimates the second moment matrix of the patch gradients.
The method determines the affine shape of the local feature as in [Baumberg00].
- Parameters:
- class kornia.feature.LAFAffineShapeEstimator(patch_size=32, affine_shape_detector=None, preserve_orientation=True)¶
Module, which extracts patches using input images and local affine frames (LAFs).
Then runs
PatchAffineShapeEstimatoron patches to estimate LAFs shape.Then original LAF shape is replaced with estimated one. The original LAF orientation is not preserved, so it is recommended to first run LAFAffineShapeEstimator and then LAFOrienter,
- Parameters:
patch_size (
int, optional) – the input image patch size. Default:32affine_shape_detector (
Optional[Module], optional) – Patch affine shape estimator,PatchAffineShapeEstimator. Default:Nonepreserve_orientation (
bool, optional) – if True, the original orientation is preserved. Default:True
- class kornia.feature.LAFOrienter(patch_size=32, num_angular_bins=36, angle_detector=None)¶
Module, which extracts patches using input images and local affine frames (LAFs).
Then runs
PatchDominantGradientOrientationorOriNeton patches and then rotates the LAFs by the estimated angles- Parameters:
patch_size (
int, optional) – Default:32num_angular_bins (
int, optional) – Default:36angle_detector (
Optional[Module], optional) – Patch orientation estimator, e.g.PatchDominantGradientOrientationor OriNet. Default:None
- class kornia.feature.PatchDominantGradientOrientation(patch_size=32, num_angular_bins=36, eps=1e-8)¶
Module, which estimates the dominant gradient orientation of the given patches, in radians.
Zero angle points towards right.
- Parameters:
- class kornia.feature.OriNet(pretrained=False, eps=1e-8)¶
Network, which estimates the canonical orientation of the given 32x32 patches, in radians.
Zero angle points towards right. This is based on the original code from paper “Repeatability Is Not Enough: Learning Discriminative Affine Regions via Discriminability””. See [MRM18] for more details.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Angle in radians.
- Shape:
Input: (B, 1, 32, 32)
Output: (B)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(16, 1, 32, 32) >>> orinet = OriNet() >>> angle = orinet(input) # 16
- class kornia.feature.LAFAffNetShapeEstimator(pretrained=False, preserve_orientation=True)¶
Module, which extracts patches using input images and local affine frames (LAFs).
Then runs AffNet on patches to estimate LAFs shape. This is based on the original code from paper “Repeatability Is Not Enough: Learning Discriminative Affine Regions via Discriminability””. See [MRM18] for more details.
Then original LAF shape is replaced with estimated one. The original LAF orientation is not preserved, so it is recommended to first run LAFAffineShapeEstimator and then LAFOrienter.
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default:False
Layers¶
- class kornia.feature.FilterResponseNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-6, is_bias=True, is_scale=True, is_eps_leanable=False)¶
Feature Response Normalization layer from ‘Filter Response Normalization Layer: Eliminating Batch Dependence in the Training of Deep Neural Networks’, see [SK20] for more details.
\[y = \gamma \times \frac{x}{\sqrt{\mathrm{E}[x^2]} + |\epsilon|} + \beta\]- Parameters:
- Returns:
Normalized features
- Return type:
- Shape:
Input: \((B, \text{num_features}, H, W)\)
Output: \((B, \text{num_features}, H, W)\)
- class kornia.feature.TLU(num_features)¶
TLU layer from ‘Filter Response Normalization Layer: Eliminating Batch Dependence in the Training of Deep Neural Networks, see [SK20] for more details. \({\tau}\) is learnable per channel.
\[y = \max(x, {\tau})\]- Parameters:
num_features (
int) – number of channels- Returns:
torch.Tensor
- Shape:
Input: \((B, \text{num_features}, H, W)\)
Output: \((B, \text{num_features}, H, W)\)
Other¶
- class kornia.feature.DeFMO(pretrained=False)¶
Module that disentangle a fast-moving object from the background and performs deblurring.
- This is based on the original code from paper “DeFMO: Deblurring and Shape Recovery
of Fast Moving Objects”. See [ROF+21] for more details.
- Parameters:
pretrained (
bool, optional) – Download and set pretrained weights to the model. Default: false.- Returns:
Temporal super-resolution without background.
- Shape:
Input: (B, 6, H, W)
Output: (B, S, 4, H, W)
Examples
>>> import kornia >>> input = torch.rand(2, 6, 240, 320) >>> defmo = kornia.feature.DeFMO() >>> tsr_nobgr = defmo(input) # 2x24x4x240x320
- forward(input_data)¶
Define the computation performed at every call.
Should be overridden by all subclasses. :rtype:
TensorNote
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the registered hooks while the latter silently ignores them.