kornia.color¶
The functions in this section perform various color space conversions.
Note
Check a tutorial for color space conversions here.
Grayscale¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grayscale
- kornia.color.rgb_to_grayscale(image, rgb_weights=None)¶
Convert a RGB image to grayscale version of image.

The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
grayscale version of the image with shape \((*,1,H,W)\).
Note
See a working example here.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> gray = rgb_to_grayscale(input) # 2x1x4x5
- kornia.color.bgr_to_grayscale(image)¶
Convert a BGR image to grayscale.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). First flips to RGB, then converts.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – BGR image to be converted to grayscale with shape \((*,3,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
grayscale version of the image with shape \((*,1,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> gray = bgr_to_grayscale(input) # 2x1x4x5
- kornia.color.grayscale_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert a grayscale image to RGB version of image.

The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – grayscale image tensor to be converted to RGB with shape \((*,1,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.randn(2, 1, 4, 5) >>> gray = grayscale_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.apply_colormap(input_tensor, colormap)
Apply to a gray tensor a colormap.

- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
A RGB tensor with the applied color map into the input_tensor.
- Raises:
ValueError – If colormap is not a ColorMap object.
Note
The image data is assumed to be integer values in range of [0-255].
Example
>>> input_tensor = torch.tensor([[[0, 1, 2], [25, 50, 63]]]) >>> colormap = ColorMap(base='autumn') >>> apply_colormap(input_tensor, colormap) tensor([[[1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000], [1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0159, 0.0317], [0.3968, 0.7937, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]])
- class kornia.color.GrayscaleToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Module to convert a grayscale image to RGB version of image.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
- reference:
https://docs.opencv.org/4.0.1/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 5) >>> rgb = GrayscaleToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToGrayscale(rgb_weights=None)¶
Module to convert a RGB image to grayscale version of image.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
- reference:
https://docs.opencv.org/4.0.1/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> gray = RgbToGrayscale() >>> output = gray(input) # 2x1x4x5
- class kornia.color.BgrToGrayscale(*args, **kwargs)¶
Module to convert a BGR image to grayscale version of image.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). First flips to RGB, then converts.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
- reference:
https://docs.opencv.org/4.0.1/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> gray = BgrToGrayscale() >>> output = gray(input) # 2x1x4x5
- class kornia.color.ApplyColorMap(colormap)
Class for applying a colormap to images.

- Parameters:
colormap (
ColorMap) – Either the name of a built-in colormap or a ColorMap object.num_colors – Number of colors in the colormap. Default is 256.
device – The device to put the generated colormap on.
dtype – The data type of the generated colormap.
- Returns:
A RGB tensor with the applied color map into the input_tensor
- Raises:
ValueError – If colormap is not a ColorMap object.
Note
The image data is assumed to be integer values in range of [0-255].
Example
>>> input_tensor = torch.tensor([[[0, 1, 2], [25, 50, 63]]]) >>> colormap = ColorMap(base='autumn') >>> ApplyColorMap(colormap=colormap)(input_tensor) tensor([[[1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000], [1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0159, 0.0317], [0.3968, 0.7937, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]])
RGB¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RGB_color_model
- kornia.color.rgb_to_bgr(image)¶
Convert a RGB image to BGR.

- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to BGRof of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
BGR version of the image with shape of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_bgr(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.bgr_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert a BGR image to RGB.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – BGR Image to be converted to BGR of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = bgr_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.rgb_to_linear_rgb(image)¶
Convert an sRGB image to linear RGB. Used in colorspace conversions.

- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – sRGB Image to be converted to linear RGB of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
linear RGB version of the image with shape of \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_linear_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.linear_rgb_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert a linear RGB image to sRGB. Used in colorspace conversions.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – linear RGB Image to be converted to sRGB of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
sRGB version of the image with shape of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = linear_rgb_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToBgr(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to BGR.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
BGR version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> bgr = RgbToBgr() >>> output = bgr(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.BgrToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert image from BGR to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = BgrToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.LinearRgbToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert a linear RGB image to sRGB.
Applies gamma correction to linear RGB values, at the end of colorspace conversions, to get sRGB.
- Returns:
sRGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> srgb = LinearRgbToRgb() >>> output = srgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
References
[1] https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35952564/convert-rgb-to-srgb
[2] https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
- class kornia.color.RgbToLinearRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from sRGB to linear RGB.
Reverses the gamma correction of sRGB to get linear RGB values for colorspace conversions. The image data is assumed to be in the range of \([0, 1]\)
- Returns:
Linear RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb_lin = RgbToLinearRgb() >>> output = rgb_lin(input) # 2x3x4x5
References
[1] https://stackoverflow.com/questions/35952564/convert-rgb-to-srgb
[2] https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
RGBA¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RGBA_color_model
- kornia.color.bgr_to_rgba(image, alpha_val)¶
Convert an image from BGR to RGBA.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
RGBA version of the image with shape \((*,4,H,W)\).
Note
The current functionality is NOT supported by Torchscript.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = bgr_to_rgba(input, 1.) # 2x4x4x5
- kornia.color.rgb_to_rgba(image, alpha_val)¶
Convert an image from RGB to RGBA.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to RGBA of shape \((*,3,H,W)\).alpha_val (float, torch.Tensor) – A float number for the alpha value or a tensor of shape \((*,1,H,W)\).
- Return type:
- Returns:
RGBA version of the image with shape \((*,4,H,W)\).
Note
The current functionality is NOT supported by Torchscript.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_rgba(input, 1.) # 2x4x4x5
- kornia.color.rgba_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert an image from RGBA to RGB.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGBA Image to be converted to RGB of shape \((*,4,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 4, 4, 5) >>> output = rgba_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.rgba_to_bgr(image)¶
Convert an image from RGBA to BGR.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGBA Image to be converted to BGR of shape \((*,4,H,W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 4, 4, 5) >>> output = rgba_to_bgr(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToRgba(alpha_val)¶
Convert an image from RGB to RGBA.
Add an alpha channel to existing RGB image.
- Parameters:
alpha_val (
Union[float,Tensor]) – A float number for the alpha value or a tensor of shape \((*,1,H,W)\).- Returns:
RGBA version of the image with shape \((*,4,H,W)\).
- Return type:
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 4, H, W)\)
Note
The current functionality is NOT supported by Torchscript.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgba = RgbToRgba(1.) >>> output = rgba(input) # 2x4x4x5
- class kornia.color.BgrToRgba(alpha_val)¶
Convert an image from BGR to RGBA.
Add an alpha channel to existing RGB image.
- Parameters:
alpha_val (
Union[float,Tensor]) – A float number for the alpha value or a tensor of shape \((*,1,H,W)\).- Returns:
RGBA version of the image with shape \((*,4,H,W)\).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 4, H, W)\)
Note
The current functionality is NOT supported by Torchscript.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgba = BgrToRgba(1.) >>> output = rgba(input) # 2x4x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbaToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGBA to RGB.
Remove an alpha channel from RGB image.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 4, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 4, 4, 5) >>> rgba = RgbaToRgb() >>> output = rgba(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbaToBgr(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGBA to BGR.
Remove an alpha channel from BGR image.
- Returns:
BGR version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 4, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 4, 4, 5) >>> rgba = RgbaToBgr() >>> output = rgba(input) # 2x3x4x5
HLS¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSL_and_HSV
- kornia.color.rgb_to_hls(image, eps=1e-8)¶
Convert an RGB image to HLS.
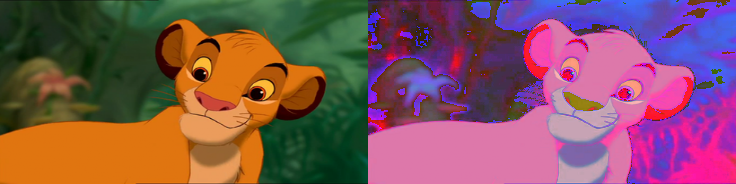
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
NOTE: this method cannot be compiled with JIT in pytohrch < 1.7.0
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
HLS version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_hls(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.hls_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert a HLS image to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – HLS image to be converted to RGB with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = hls_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToHls(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to HLS.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
HLS version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> hls = RgbToHls() >>> output = hls(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.HlsToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from HLS to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
input: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
- Reference:
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = HlsToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
HSV¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HSL_and_HSV
- kornia.color.rgb_to_hsv(image, eps=1e-8)¶
Convert an image from RGB to HSV.

The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
HSV version of the image with shape of \((*, 3, H, W)\). The H channel values are in the range 0..2pi. S and V are in the range 0..1.
Note
See a working example here.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_hsv(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.hsv_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert an image from HSV to RGB.
The H channel values are assumed to be in the range 0..2pi. S and V are in the range 0..1.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – HSV Image to be converted to HSV with shape of \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape of \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = hsv_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToHsv(eps=1e-6)¶
Convert an image from RGB to HSV.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
eps (
float, optional) – scalar to enforce numarical stability. Default:1e-6- Returns:
HSV version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> hsv = RgbToHsv() >>> output = hsv(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.HsvToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from HSV to RGB.
H channel values are assumed to be in the range 0..2pi. S and V are in the range 0..1.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = HsvToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
LUV¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIELUV
- kornia.color.rgb_to_luv(image, eps=1e-12)¶
Convert a RGB image to Luv.

The image data is assumed to be in the range of \([0, 1]\). Luv color is computed using the D65 illuminant and Observer 2.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Luv version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_luv(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.luv_to_rgb(image, eps=1e-12)¶
Convert a Luv image to RGB.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Luv version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = luv_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToLuv(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to Luv.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of \([0, 1]\). Luv color is computed using the D65 illuminant and Observer 2.
- Returns:
Luv version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> luv = RgbToLuv() >>> output = luv(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.LuvToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from Luv to RGB.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = LuvToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
References
[1] https://docs.opencv.org/4.0.1/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html
Lab¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIELAB_color_space
- kornia.color.rgb_to_lab(image)¶
Convert a RGB image to Lab.

The input RGB image is assumed to be in the range of \([0, 1]\). Lab color is computed using the D65 illuminant and Observer 2.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to Lab with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
Lab version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\). The L channel values are in the range 0..100. a and b are in the range -128..127.
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_lab(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.lab_to_rgb(image, clip=True)¶
Convert a Lab image to RGB.
The L channel is assumed to be in the range of \([0, 100]\). a and b channels are in the range of \([-128, 127]\).
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
Lab version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\). The output RGB image are in the range of \([0, 1]\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = lab_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToLab(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to Lab.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of \([0, 1]\). Lab color is computed using the D65 illuminant and Observer 2.
- Returns:
Lab version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> lab = RgbToLab() >>> output = lab(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.LabToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from Lab to RGB.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image. Range may not be in \([0, 1]\).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = LabToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
References
[1] https://docs.opencv.org/4.0.1/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html
[2] https://www.easyrgb.com/en/math.php
[3] https://github.com/torch/image/blob/dc061b98fb7e946e00034a5fc73e883a299edc7f/generic/image.c#L1518
YCbCr¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YCbCr
- kornia.color.rgb_to_ycbcr(image)¶
Convert an RGB image to YCbCr.

- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to YCbCr with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
YCbCr version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_ycbcr(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.ycbcr_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert an YCbCr image to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – YCbCr Image to be converted to RGB with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = ycbcr_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.YcbcrToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from YCbCr to Rgb.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = YcbcrToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToYcbcr(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to YCbCr.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
YCbCr version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> ycbcr = RgbToYcbcr() >>> output = ycbcr(input) # 2x3x4x5
YUV¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV
- kornia.color.rgb_to_yuv(image)¶
Convert an RGB image to YUV.

The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to YUV with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
YUV version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_yuv(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.yuv_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert an YUV image to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1) for luma and (-0.5, 0.5) for chroma.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – YUV Image to be converted to RGB with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = yuv_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToYuv(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to YUV.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
YUV version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> yuv = RgbToYuv() >>> output = yuv(input) # 2x3x4x5
- Reference::
- class kornia.color.YuvToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from YUV to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1) for luma and (-0.5, 0.5) for chroma.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = YuvToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
YUV420¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroma_subsampling
- kornia.color.rgb_to_yuv420(image)¶
Convert an RGB image to YUV 420 (subsampled).
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). Input need to be padded to be evenly divisible by 2 horizontal and vertical. This function will output chroma siting (0.5,0.5)
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to YUV with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
A Tensor containing the Y plane with shape \((*, 1, H, W)\) A Tensor containing the UV planes with shape \((*, 2, H/2, W/2)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 6) >>> output = rgb_to_yuv420(input) # (2x1x4x6, 2x2x2x3)
- kornia.color.yuv420_to_rgb(imagey, imageuv)¶
Convert an YUV420 image to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1) for luma and (-0.5, 0.5) for chroma. Input need to be padded to be evenly divisible by 2 horizontal and vertical. This function assumed chroma siting is (0.5, 0.5)
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> inputy = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> inputuv = torch.rand(2, 2, 2, 3) >>> output = yuv420_to_rgb(inputy, inputuv) # 2x3x4x6
- class kornia.color.RgbToYuv420(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to YUV420.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). Width and Height evenly divisible by 2.
- Returns:
YUV420 version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 1, H, W)\) and \((*, 2, H/2, W/2)\)
Examples
>>> yuvinput = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 6) >>> yuv = RgbToYuv420() >>> output = yuv(yuvinput) # # (2x1x4x6, 2x1x2x3)
- Reference::
- class kornia.color.Yuv420ToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from YUV to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1) for luma and (-0.5, 0.5) for chroma. Width and Height evenly divisible by 2.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
imagey: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
imageuv: \((*, 2, H/2, W/2)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> inputy = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> inputuv = torch.rand(2, 2, 2, 3) >>> rgb = Yuv420ToRgb() >>> output = rgb(inputy, inputuv) # 2x3x4x6
YUV422¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroma_subsampling
- kornia.color.rgb_to_yuv422(image)¶
Convert an RGB image to YUV 422 (subsampled).
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). Input need to be padded to be evenly divisible by 2 vertical. This function will output chroma siting (0.5)
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to YUV with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
A Tensor containing the Y plane with shape \((*, 1, H, W)\) A Tensor containing the UV planes with shape \((*, 2, H, W/2)\)
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 6) >>> output = rgb_to_yuv420(input) # (2x1x4x6, 2x1x4x3)
- kornia.color.yuv422_to_rgb(imagey, imageuv)¶
Convert an YUV422 image to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1) for luma and (-0.5, 0.5) for chroma. Input need to be padded to be evenly divisible by 2 vertical. This function assumed chroma siting is (0.5)
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> inputy = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> inputuv = torch.rand(2, 2, 2, 3) >>> output = yuv420_to_rgb(inputy, inputuv) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToYuv422(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to YUV422.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). Width evenly disvisible by 2.
- Returns:
YUV422 version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 1, H, W)\) and \((*, 2, H, W/2)\)
Examples
>>> yuvinput = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 6) >>> yuv = RgbToYuv422() >>> output = yuv(yuvinput) # # (2x1x4x6, 2x2x4x3)
- Reference::
- class kornia.color.Yuv422ToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from YUV to RGB.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1) for luma and (-0.5, 0.5) for chroma. Width evenly divisible by 2.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
imagey: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
imageuv: \((*, 2, H, W/2)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> inputy = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> inputuv = torch.rand(2, 2, 4, 3) >>> rgb = Yuv422ToRgb() >>> output = rgb(inputy, inputuv) # 2x3x4x6
XYZ¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CIELUV
- kornia.color.rgb_to_xyz(image)¶
Convert a RGB image to XYZ.
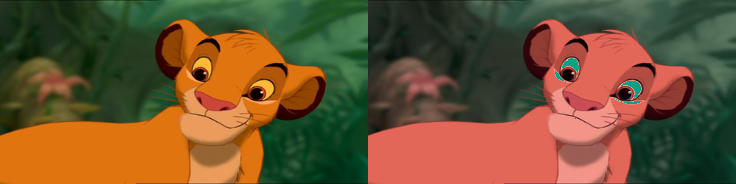
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – RGB Image to be converted to XYZ with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
XYZ version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = rgb_to_xyz(input) # 2x3x4x5
- kornia.color.xyz_to_rgb(image)¶
Convert a XYZ image to RGB.
- Parameters:
image (
Tensor) – XYZ Image to be converted to RGB with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*, 3, H, W)\).
Example
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> output = xyz_to_rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToXyz(*args, **kwargs)¶
Convert an image from RGB to XYZ.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Returns:
XYZ version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> xyz = RgbToXyz() >>> output = xyz(input) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.XyzToRgb(*args, **kwargs)¶
Converts an image from XYZ to RGB.
- Returns:
RGB version of the image.
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Examples
>>> input = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 5) >>> rgb = XyzToRgb() >>> output = rgb(input) # 2x3x4x5
Bayer RAW¶
Tip
Learn more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bayer_filter
- class kornia.color.CFA(value, names=None, *, module=None, qualname=None, type=None, start=1, boundary=None)¶
Define the configuration of the color filter array.
So far only bayer images is supported and the enum sets the pixel order for bayer. Note that this can change due to things like rotations and cropping of images. Take care if including the translations in pipeline. This implementations is optimized to be reasonably fast, look better than simple nearest neighbour. On top of this care is taken to make it reversible going raw -> rgb -> raw. the raw samples remain intact during conversion and only unknown samples are interpolated.
The names are based on the OpenCV convention where the BG indicates pixel 1,1 (counting from 0,0) is blue and its neighbour to the right is green. In that case the top left pixel is red. Other options are GB, RG and GR
- BG = 0¶
- GB = 1¶
- GR = 3¶
- RG = 2¶
- kornia.color.rgb_to_raw(image, cfa)¶
Convert a RGB image to RAW version of image with the specified color filter array.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
raw version of the image with shape \((*,1,H,W)\).
Example
>>> rgbinput = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 6) >>> raw = rgb_to_raw(rgbinput, CFA.BG) # 2x1x4x6
- kornia.color.raw_to_rgb(image, cfa)¶
Convert a raw bayer image to RGB version of image.
We are assuming a CFA with 2 green, 1 red, 1 blue. A bilinear interpolation is used for R/G and a fix convolution for the green pixels. To simplify calculations we expect the Height Width to be evenly divisible by 2.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). Image H/W is assumed to be evenly divisible by 2. for simplicity reasons
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
RGB version of the image with shape \((*,3,H,W)\).
Example
>>> rawinput = torch.randn(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> rgb = raw_to_rgb(rawinput, CFA.RG) # 2x3x4x6
- kornia.color.raw_to_rgb_2x2_downscaled(image, cfa)¶
Convert the raw bayer image to RGB version of it and resize width and height by half.
This is done efficiently by converting each superpixel of bayer image to the corresponding rgb triplet. R and B channels of the raw image are left as are, while two G channels of raw image are averaged to obtain the output G channel.
We are assuming a CFA with 2 green, 1 red, 1 blue. The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1). Image H/W is assumed to be evenly divisible by 2 for simplicity reasons.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
downscaled RGB version of the image with shape \((*,3,\frac{H}{2},\frac{W}{2})\).
Example
>>> rawinput = torch.randn(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> rgb = raw_to_rgb_2x2_downscaled(rawinput, CFA.RG) # 2x3x2x3
- class kornia.color.RawToRgb(cfa)¶
Module to convert a bayer raw image to RGB version of image.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
Example
>>> rawinput = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> rgb = RawToRgb(CFA.RG) >>> output = rgb(rawinput) # 2x3x4x5
- class kornia.color.RgbToRaw(cfa)¶
Module to convert a RGB image to bayer raw version of image.
The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 3, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
- reference:
https://docs.opencv.org/4.0.1/de/d25/imgproc_color_conversions.html
Example
>>> rgbinput = torch.rand(2, 3, 4, 6) >>> raw = RgbToRaw(CFA.GB) >>> output = raw(rgbinput) # 2x1x4x6
- class kornia.color.RawToRgb2x2Downscaled(cfa)¶
Module version of the
raw_to_rgb_2x2_downscaled()function.The image width and height have to be divisible by two. The image data is assumed to be in the range of (0, 1).
- Shape:
image: \((*, 1, H, W)\)
output: \((*, 3, \frac{H}{2}, \frac{W}{2})\)
Example
>>> rawinput = torch.rand(2, 1, 4, 6) >>> rgb_downscale = RawToRgb2x2Downscaled(CFA.RG) >>> output = rgb_downscale(rawinput) # 2x3x2x3
Sepia¶
- class kornia.color.Sepia(rescale=True, eps=1e-6)¶
Module that apply the sepia filter to tensors.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The sepia tensor of same size and numbers of channels as the input with shape \((*, C, H, W)\).
- Return type:
Tensor
Example
>>> >>> input = torch.ones(3, 1, 1) >>> Sepia(rescale=False)(input) tensor([[[1.3510]], [[1.2030]], [[0.9370]]])
- kornia.color.sepia(input, rescale=True, eps=1e-6)¶
Apply to a tensor the sepia filter.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The sepia tensor of same size and numbers of channels as the input with shape \((*, C, H, W)\).
- Return type:
Tensor
Example
>>> input = torch.ones(3, 1, 1) >>> sepia_from_rgb(input, rescale=False) tensor([[[1.3510]], [[1.2030]], [[0.9370]]])
Color Maps¶
- class kornia.color.ColorMap(base, num_colors=64, device=None, dtype=None)¶
Class to represent a colour map. It can be created or selected from the built-in colour map. Please refer to the ColorMapType enum class to view all available colormaps.
- Parameters:
base (
Union[list[List[float]],str,ColorMapType]) – A list of RGB colors to define a new custom colormap orclass. (the name of a built-in colormap as str or using ColorMapType)
num_colors (
int, optional) – Number of colors in the colormap. Default:64device (
Optional[device], optional) – The device to put the generated colormap on. Default:Nonedtype (
Optional[dtype], optional) – The data type of the generated colormap. Default:None
- Returns:
An object of the colormap with the num_colors length.
Examples
>>> ColorMap(base='viridis', num_colors=8).colors tensor([[0.2813, 0.2621, 0.2013, 0.1505, 0.1210, 0.2463, 0.5259, 0.8557], [0.0842, 0.2422, 0.3836, 0.5044, 0.6258, 0.7389, 0.8334, 0.8886], [0.4072, 0.5207, 0.5543, 0.5574, 0.5334, 0.4519, 0.2880, 0.0989]])
- Create a color map from the first color (RGB with range[0-1]) to the last one with num_colors length.
>>> ColorMap(base=[[0., 0.5 , 1.0], [1., 0.5, 0.]], num_colors=8).colors tensor([[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.1250, 0.3750, 0.6250, 0.8750, 1.0000, 1.0000], [0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000, 0.5000], [1.0000, 1.0000, 0.8750, 0.6250, 0.3750, 0.1250, 0.0000, 0.0000]])
Color maps available:
- class kornia.color.ColorMapType(value, names=None, *, module=None, qualname=None, type=None, start=1, boundary=None)¶
An enumeration for available colormaps.
List of available colormaps:
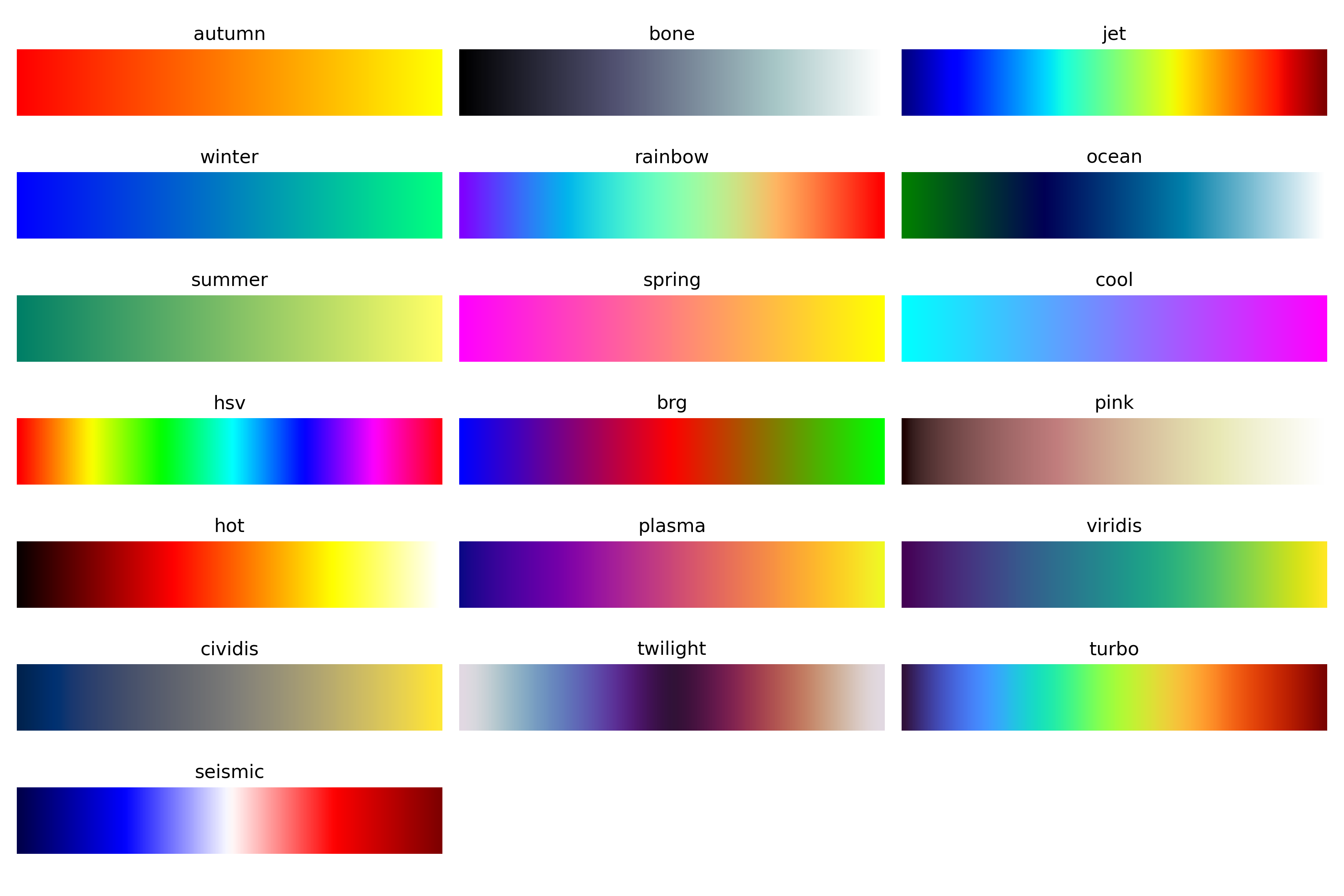
- autumn = 1¶
- bone = 2¶
- jet = 3¶
- winter = 4¶
- rainbow = 5¶
- ocean = 6¶
- summer = 7¶
- spring = 8¶
- cool = 9¶
- hsv = 10¶
- brg = 11¶
- pink = 12¶
- hot = 13¶
- plasma = 14¶
- viridis = 15¶
- cividis = 16¶
- twilight = 17¶
- turbo = 18¶
- seismic = 19¶
Functions and modules to use the color maps:
- kornia.color.apply_colormap(input_tensor, colormap)¶
Apply to a gray tensor a colormap.

- Parameters:
- Return type:
- Returns:
A RGB tensor with the applied color map into the input_tensor.
- Raises:
ValueError – If colormap is not a ColorMap object.
Note
The image data is assumed to be integer values in range of [0-255].
Example
>>> input_tensor = torch.tensor([[[0, 1, 2], [25, 50, 63]]]) >>> colormap = ColorMap(base='autumn') >>> apply_colormap(input_tensor, colormap) tensor([[[1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000], [1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0159, 0.0317], [0.3968, 0.7937, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]])
- class kornia.color.ApplyColorMap(colormap)¶
Class for applying a colormap to images.

- Parameters:
colormap (
ColorMap) – Either the name of a built-in colormap or a ColorMap object.num_colors – Number of colors in the colormap. Default is 256.
device – The device to put the generated colormap on.
dtype – The data type of the generated colormap.
- Returns:
A RGB tensor with the applied color map into the input_tensor
- Raises:
ValueError – If colormap is not a ColorMap object.
Note
The image data is assumed to be integer values in range of [0-255].
Example
>>> input_tensor = torch.tensor([[[0, 1, 2], [25, 50, 63]]]) >>> colormap = ColorMap(base='autumn') >>> ApplyColorMap(colormap=colormap)(input_tensor) tensor([[[1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000], [1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0159, 0.0317], [0.3968, 0.7937, 1.0000]], [[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]])