kornia.geometry.liegroup#
The Lie group encompasses the concepts of group and smooth manifold in a unique body.
A group is a non-empty set with an operation that satisfies the following constraints: the operation is associative, has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element.
See more: Group
A Lie group \(G\) is a smooth manifold whose elements satisfy the group axioms.You can visualize the idea of manifold like a curved, smooth (hyper)-surface, with no edges or spikes, embedded in a space of higher dimension.
See more: Manifold
In robotics, we say that our state vector evolves on this surface, that is, the manifold describes or is defined by the constraints imposed on the state.
lie algebra#
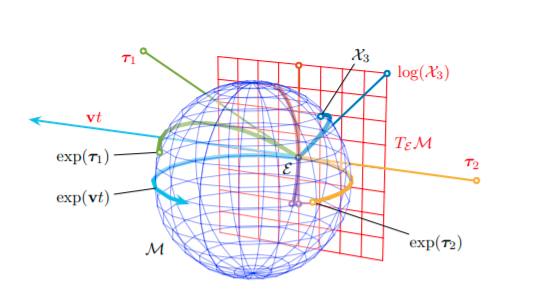
If \(M\) is the manifold that represents a lie group, the tangent space at the identity is called the Lie algebra of \(M\). The Lie algebra \(m\) is a vector space. As such, its elements can be identified with vectors in \(R^d\), whose dimension \(d\) is the number of degrees of freedom of \(M\). For example \(d\) would be 3 in the case of lie group \(SO3\)
lie group and lie algebra#
Every Lie group has an associated Lie algebra. We relate the Lie group with its Lie algebra through the following facts
The Lie algebra \(m\) is a vector space. As such, its elements can be identified with vectors in \(R^d\), whose dimension \(d\) is the number of degrees of freedom of \(M\).
The exponential map, exp : \(m\) → \(M\), exactly converts elements of the Lie algebra into elements of the group. The log map is the inverse operation.
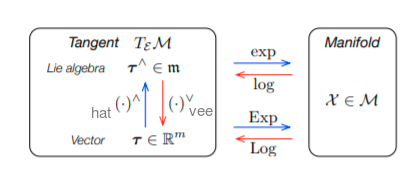
Reference: Micro lie theory
- class kornia.geometry.liegroup.So3(q)#
Base class to represent the So3 group.
The SO(3) is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \(R^3\) under the operation of composition. See more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/3D_rotation_group
We internally represent the rotation by a unit quaternion.
Example
>>> q = Quaternion.identity() >>> s = So3(q) >>> s.q Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
- static Jl(vec)#
Alias for left jacobian.
- static Jr(vec)#
Alias for right jacobian.
- __init__(q)#
Constructor for the base class.
Internally represented by a unit quaternion q.
- Parameters:
data – Quaternion with the shape of \((B, 4)\).
Example
>>> data = torch.ones((2, 4)) >>> q = Quaternion(data) >>> So3(q) Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
- __mul__(right)#
Compose two So3 transformations.
- adjoint()#
Returns the adjoint matrix of shape \((B, 3, 3)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So3.identity() >>> s.adjoint() tensor([[1., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 1.]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
- static exp(v)#
Converts elements of lie algebra to elements of lie group.
See more: https://vision.in.tum.de/_media/members/demmeln/nurlanov2021so3log.pdf
Example
>>> v = torch.zeros((2, 3)) >>> s = So3.exp(v) >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [1., 0., 0., 0.]], requires_grad=True)
- classmethod from_matrix(matrix)#
Create So3 from a rotation matrix.
Example
>>> m = torch.eye(3) >>> s = So3.from_matrix(m) >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
- classmethod from_wxyz(wxyz)#
Create So3 from a tensor representing a quaternion.
Example
>>> q = torch.tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.]) >>> s = So3.from_wxyz(q) >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
- static hat(v)#
Converts elements from vector space to lie algebra. Returns matrix of shape \((B,3,3)\).
Example
>>> v = torch.ones((1,3)) >>> m = So3.hat(v) >>> m tensor([[[ 0., -1., 1.], [ 1., 0., -1.], [-1., 1., 0.]]])
- classmethod identity(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a So3 group representing an identity rotation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So3.identity() >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
>>> s = So3.identity(batch_size=2) >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.], [1., 0., 0., 0.]], requires_grad=True)
- inverse()#
Returns the inverse transformation.
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So3.identity() >>> s.inverse() Parameter containing: tensor([1., -0., -0., -0.], requires_grad=True)
- static left_jacobian(vec)#
Computes the left Jacobian of So3.
Example
>>> vec = torch.tensor([1., 2., 3.]) >>> So3.left_jacobian(vec) tensor([[-0.0687, -0.2267, 0.5074], [ 0.5556, 0.1779, 0.3629], [-0.0141, 0.6236, 0.5890]])
- log()#
Converts elements of lie group to elements of lie algebra.
- Return type:
Example
>>> data = torch.ones((2, 4)) >>> q = Quaternion(data) >>> So3(q).log() tensor([[0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.]], grad_fn=<WhereBackward0>)
- matrix()#
Convert the quaternion to a rotation matrix of shape \((B,3,3)\).
The matrix is of the form: :rtype:
Tensor\[\begin{split}\begin{bmatrix} 1-2y^2-2z^2 & 2xy-2zw & 2xy+2yw \\ 2xy+2zw & 1-2x^2-2z^2 & 2yz-2xw \\ 2xz-2yw & 2yz+2xw & 1-2x^2-2y^2\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]Example
>>> s = So3.identity() >>> m = s.matrix() >>> m tensor([[1., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 1.]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
- property q: Quaternion#
Return the underlying data with shape \((B,4)\).
- classmethod random(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a So3 group representing a random rotation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So3.random() >>> s = So3.random(batch_size=3)
- static right_jacobian(vec)#
Computes the right Jacobian of So3.
Example
>>> vec = torch.tensor([1., 2., 3.]) >>> So3.right_jacobian(vec) tensor([[-0.0687, 0.5556, -0.0141], [-0.2267, 0.1779, 0.6236], [ 0.5074, 0.3629, 0.5890]])
- classmethod rot_x(x)#
Construct a x-axis rotation.
- classmethod rot_y(y)#
Construct a z-axis rotation.
- classmethod rot_z(z)#
Construct a z-axis rotation.
- static vee(omega)#
Converts elements from lie algebra to vector space. Returns vector of shape \((B,3)\).
\[\begin{split}omega = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & -c & b \\ c & 0 & -a \\ -b & a & 0\end{bmatrix}\end{split}\]Example
>>> v = torch.ones((1,3)) >>> omega = So3.hat(v) >>> So3.vee(omega) tensor([[1., 1., 1.]])
- class kornia.geometry.liegroup.Se3(rotation, translation)#
Base class to represent the Se3 group.
The SE(3) is the group of rigid body transformations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space \(R^3\) under the operation of composition. See more: https://ingmec.ual.es/~jlblanco/papers/jlblanco2010geometry3D_techrep.pdf
Example
>>> q = Quaternion.identity() >>> s = Se3(q, torch.ones(3)) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t Parameter containing: tensor([1., 1., 1.], requires_grad=True)
- __init__(rotation, translation)#
Constructor for the base class.
Internally represented by a unit quaternion q and a translation 3-vector.
- Parameters:
rotation (
Quaternion|So3) – So3 group encompassing a rotation.translation (
Vector3|Tensor) – Vector3 or translation tensor with the shape of \((B, 3)\).
Example
>>> from kornia.geometry.quaternion import Quaternion >>> q = Quaternion.identity(batch_size=1) >>> s = Se3(q, torch.ones((1, 3))) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.]], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
- __mul__(right)#
Compose two Se3 transformations.
- adjoint()#
Returns the adjoint matrix of shape \((B, 6, 6)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se3.identity() >>> s.adjoint() tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]], grad_fn=<CatBackward0>)
- static exp(v)#
Converts elements of lie algebra to elements of lie group.
Example
>>> v = torch.zeros((1, 6)) >>> s = Se3.exp(v) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.]], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t Parameter containing: tensor([[0., 0., 0.]], requires_grad=True)
- classmethod from_matrix(matrix)#
Create a Se3 group from a matrix.
Example
>>> s = Se3.from_matrix(torch.eye(4)) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t Parameter containing: tensor([0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True)
- classmethod from_qxyz(qxyz)#
Create a Se3 group a quaternion and translation vector.
Example
>>> qxyz = torch.tensor([1., 2., 3., 0., 0., 0., 1.]) >>> s = Se3.from_qxyz(qxyz) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([1., 2., 3., 0.], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t x: 0.0 y: 0.0 z: 1.0
- static hat(v)#
Converts elements from vector space to lie algebra.
- Parameters:
v (
Tensor) – vector of shape \((B, 6)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
matrix of shape \((B, 4, 4)\).
Example
>>> v = torch.ones((1, 6)) >>> m = Se3.hat(v) >>> m tensor([[[ 0., -1., 1., 1.], [ 1., 0., -1., 1.], [-1., 1., 0., 1.], [ 0., 0., 0., 0.]]])
- classmethod identity(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a Se3 group representing an identity rotation and zero translation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se3.identity() >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([1., 0., 0., 0.], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t x: 0.0 y: 0.0 z: 0.0
- inverse()#
Returns the inverse transformation.
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se3(So3.identity(), torch.ones(3)) >>> s_inv = s.inverse() >>> s_inv.r Parameter containing: tensor([1., -0., -0., -0.], requires_grad=True) >>> s_inv.t Parameter containing: tensor([-1., -1., -1.], requires_grad=True)
- log()#
Converts elements of lie group to elements of lie algebra.
- Return type:
Example
>>> from kornia.geometry.quaternion import Quaternion >>> q = Quaternion.identity() >>> Se3(q, torch.zeros(3)).log() tensor([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.], grad_fn=<CatBackward0>)
- matrix()#
Returns the matrix representation of shape \((B, 4, 4)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se3(So3.identity(), torch.ones(3)) >>> s.matrix() tensor([[1., 0., 0., 1.], [0., 1., 0., 1.], [0., 0., 1., 1.], [0., 0., 0., 1.]], grad_fn=<CopySlices>)
- property quaternion: Quaternion#
Return the underlying rotation(Quaternion).
- classmethod random(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a Se3 group representing a random transformation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se3.random() >>> s = Se3.random(batch_size=3)
- classmethod rot_x(x)#
Construct a x-axis rotation.
- classmethod rot_y(y)#
Construct a y-axis rotation.
- classmethod rot_z(z)#
Construct a z-axis rotation.
- classmethod trans(x, y, z)#
Construct a translation only Se3 instance.
- classmethod trans_x(x)#
Construct a x-axis translation.
- classmethod trans_y(y)#
Construct a y-axis translation.
- classmethod trans_z(z)#
Construct a z-axis translation.
- property translation: Vector3 | Tensor#
Return the underlying translation vector of shape \((B,3)\).
- static vee(omega)#
Converts elements from lie algebra to vector space.
- Parameters:
omega (
Tensor) – 4x4-matrix representing lie algebra of shape \((B,4,4)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
vector of shape \((B,6)\).
Example
>>> v = torch.ones((1, 6)) >>> omega_hat = Se3.hat(v) >>> Se3.vee(omega_hat) tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
- class kornia.geometry.liegroup.So2(z)#
Base class to represent the So2 group.
The SO(2) is the group of all rotations about the origin of two-dimensional Euclidean space \(R^2\) under the operation of composition. See more: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orthogonal_group#Special_orthogonal_group
We internally represent the rotation by a complex number.
Example
>>> real = torch.tensor([1.0]) >>> imag = torch.tensor([2.0]) >>> So2(torch.complex(real, imag)) Parameter containing: tensor([1.+2.j], requires_grad=True)
- __init__(z)#
Constructor for the base class.
Internally represented by complex number z.
- Parameters:
z (
Tensor) – Complex number with the shape of \((B, 1)\) or \((B)\).
Example
>>> real = torch.tensor(1.0) >>> imag = torch.tensor(2.0) >>> So2(torch.complex(real, imag)).z Parameter containing: tensor(1.+2.j, requires_grad=True)
- __mul__(right)#
Performs a left-multiplication either rotation concatenation or point-transform.
- adjoint()#
Returns the adjoint matrix of shape \((B, 2, 2)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So2.identity() >>> s.adjoint() tensor([[1., -0.], [0., 1.]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
- static exp(theta)#
Converts elements of lie algebra to elements of lie group.
Example
>>> v = torch.tensor([3.1415/2]) >>> s = So2.exp(v) >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([4.6329e-05+1.j], requires_grad=True)
- classmethod from_matrix(matrix)#
Create So2 from a rotation matrix.
- Parameters:
matrix (
Tensor) – the rotation matrix to convert of shape \((B, 2, 2)\).- Return type:
Example
>>> m = torch.eye(2) >>> s = So2.from_matrix(m) >>> s.z Parameter containing: tensor(1.+0.j, requires_grad=True)
- static hat(theta)#
Converts elements from vector space to lie algebra. Returns matrix of shape \((B, 2, 2)\).
Example
>>> theta = torch.tensor(3.1415/2) >>> So2.hat(theta) tensor([[0.0000, 1.5707], [1.5707, 0.0000]])
- classmethod identity(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a So2 group representing an identity rotation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So2.identity(batch_size=2) >>> s Parameter containing: tensor([1.+0.j, 1.+0.j], requires_grad=True)
- inverse()#
Returns the inverse transformation.
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So2.identity() >>> s.inverse().z Parameter containing: tensor(1.+0.j, requires_grad=True)
- log()#
Converts elements of lie group to elements of lie algebra.
- Return type:
Example
>>> real = torch.tensor([1.0]) >>> imag = torch.tensor([3.0]) >>> So2(torch.complex(real, imag)).log() tensor([1.2490], grad_fn=<Atan2Backward0>)
- matrix()#
Convert the complex number to a rotation matrix of shape \((B, 2, 2)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So2.identity() >>> m = s.matrix() >>> m tensor([[1., -0.], [0., 1.]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
- classmethod random(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a So2 group representing a random rotation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = So2.random() >>> s = So2.random(batch_size=3)
- static vee(omega)#
Converts elements from lie algebra to vector space. Returns vector of shape \((B,)\).
Example
>>> v = torch.ones(3) >>> omega = So2.hat(v) >>> So2.vee(omega) tensor([1., 1., 1.])
- class kornia.geometry.liegroup.Se2(rotation, translation)#
Base class to represent the Se2 group.
The SE(2) is the group of rigid body transformations about the origin of two-dimensional Euclidean space \(R^2\) under the operation of composition. See more:
Example
>>> so2 = So2.identity(1) >>> t = torch.ones((1, 2)) >>> se2 = Se2(so2, t) >>> se2 rotation: Parameter containing: tensor([1.+0.j], requires_grad=True) translation: Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
- __init__(rotation, translation)#
Constructor for the base class.
Internally represented by a complex number z and a translation 2-vector.
- Parameters:
Example
>>> so2 = So2.identity(1) >>> t = torch.ones((1, 2)) >>> se2 = Se2(so2, t) >>> se2 rotation: Parameter containing: tensor([1.+0.j], requires_grad=True) translation: Parameter containing: tensor([[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
- __mul__(right)#
Compose two Se2 transformations.
- adjoint()#
Returns the adjoint matrix of shape \((B, 3, 3)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se2.identity() >>> s.adjoint() tensor([[1., -0., 0.], [0., 1., -0.], [0., 0., 1.]], grad_fn=<CopySlices>)
- static exp(v)#
Converts elements of lie algebra to elements of lie group.
Example
>>> v = torch.ones((1, 3)) >>> s = Se2.exp(v) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([0.5403+0.8415j], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t Parameter containing: tensor([[0.3818, 1.3012]], requires_grad=True)
- classmethod from_matrix(matrix)#
Create an Se2 group from a matrix.
Example
>>> s = Se2.from_matrix(torch.eye(3).repeat(2, 1, 1)) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([1.+0.j, 1.+0.j], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t Parameter containing: tensor([[0., 0.], [0., 0.]], requires_grad=True)
- static hat(v)#
Converts elements from vector space to lie algebra. Returns matrix of shape \((B, 3, 3)\).
Example
>>> theta = torch.tensor(3.1415/2) >>> So2.hat(theta) tensor([[0.0000, 1.5707], [1.5707, 0.0000]])
- classmethod identity(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a Se2 group representing an identity rotation and zero translation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se2.identity(1) >>> s.r Parameter containing: tensor([1.+0.j], requires_grad=True) >>> s.t x: tensor([0.]) y: tensor([0.])
- inverse()#
Returns the inverse transformation.
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se2(So2.identity(1), torch.ones(1,2)) >>> s_inv = s.inverse() >>> s_inv.r Parameter containing: tensor([1.+0.j], requires_grad=True) >>> s_inv.t Parameter containing: tensor([[-1., -1.]], requires_grad=True)
- log()#
Converts elements of lie group to elements of lie algebra.
- Return type:
Example
>>> v = torch.ones((1, 3)) >>> s = Se2.exp(v).log() >>> s tensor([[1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
- matrix()#
Returns the matrix representation of shape \((B, 3, 3)\).
- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se2(So2.identity(1), torch.ones(1, 2)) >>> s.matrix() tensor([[[1., -0., 1.], [0., 1., 1.], [0., 0., 1.]]], grad_fn=<CopySlices>)
- classmethod random(batch_size=None, device=None, dtype=None)#
Create a Se2 group representing a random transformation.
- Parameters:
batch_size (
Optional[int], optional) – the batch size of the underlying data. Default:None- Return type:
Example
>>> s = Se2.random() >>> s = Se2.random(batch_size=3)
- classmethod trans(x, y)#
Construct a translation only Se2 instance.
- classmethod trans_x(x)#
Construct a x-axis translation.
- classmethod trans_y(y)#
Construct a y-axis translation.
- property translation: Vector2 | Parameter#
Return the underlying translation vector of shape \((B,2)\).
- static vee(omega)#
Converts elements from lie algebra to vector space.
- Parameters:
omega (
Tensor) – 3x3-matrix representing lie algebra of shape \((B, 3, 3)\).- Return type:
- Returns:
vector of shape \((B, 3)\).
Example
>>> v = torch.ones(3) >>> omega_hat = Se2.hat(v) >>> Se2.vee(omega_hat) tensor([1., 1., 1.])